Figure 8.
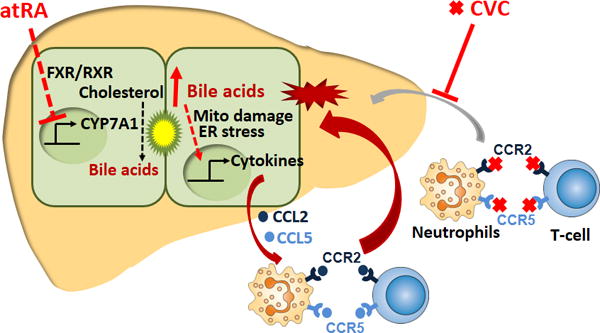
An illustration of the proposed mechanisms of action of atRA and CVC in the treatment of cholestatic liver injury. atRA activates the nuclear receptor FXR/RXR which in turn represses the expression of CYP7A1 (the rate limiting enzyme in bile acid synthesis) resulting in a lower bile acid pool size. At the same time, CVC antagonizes the chemokine receptors CCR2 and CCR5 that are present on neutrophils and T cells thereby reducing their attraction to the stressed hepatocytes that are being stimulated by bile acids to release chemokines CCL2 and CCL5.
