Figure 6.
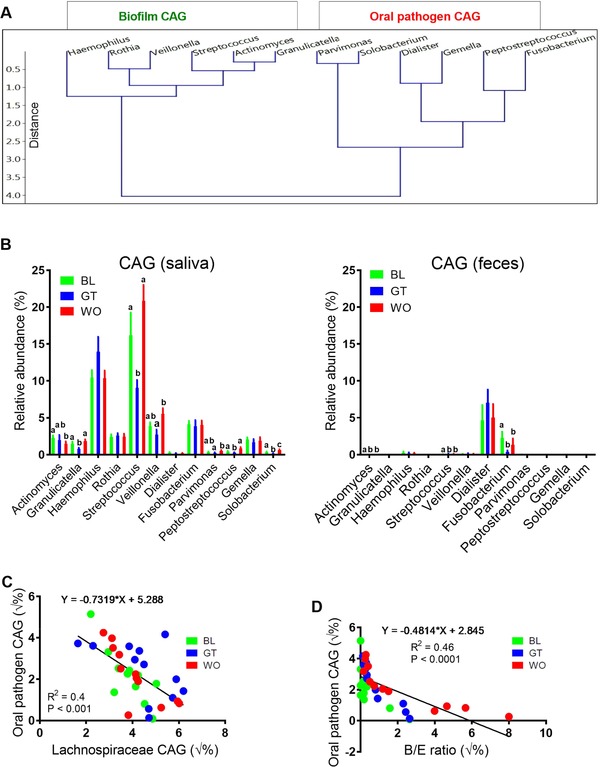
Higher fecal Lachnospiraceae and B/E ratio were negatively associated with colonization of gut with oral‐like bacterial networks. A) Hierarchical Ward‐linkage clustering based on the Pearson correlation coefficients of the RA of genus level OTUs in fecal microbiota of 12 healthy subjects. Data from all three time points were combined for this analysis. Oral biofilm co‐abundance groups (CAGs) and oral pathogen CAGs were defined on the basis of a recently published literature (please refer main text). B) Results showing comparative analysis performed between members of salivary biofilm and pathogen CAGs and oral‐like bacterial genera (members of both CAGs) present in feces using RA of genus level OTUs. C,D) Linear regression analysis showing an association between oral pathogen CAG and Lachnospiraceae CAG and between oral pathogen CAG and B/E ratio using the sqrt transformed RA of members these two CAGs identified in the whole fecal microbiota data profile. Data are expressed as means ± standard errors of the means (SEM). Data with different superscript letters are significantly different (p < 0.05) by Wilcoxon matched‐pairs signed rank test. n = 12. RA, relative abundance; OTUs, operational taxonomic units; CAGs, co‐abundance groups; B/E Bifidobacterium to Enterobacteriacea ratio; √%, square root transformed percentage values. p < 0.05 considered significant.
