Figure 1.
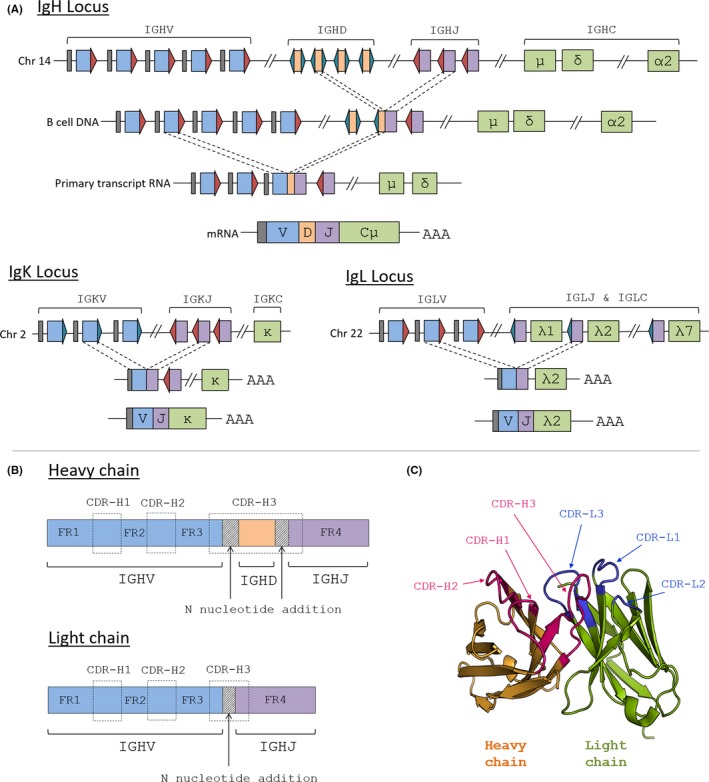
(a) Variable (V), Diversity (D) and Joining (J) gene segments are arranged in a non‐functional state in the germline. During V(D)J recombination, a V, a D and a J gene segment (just V and J in the case of light chains) are brought together at random. RSS sequences ensure gene segments are recombined in the correct order to form a functional variable region sequence. Blue, orange and purple rectangles represent V, D, and J gene segments, respectively, with gray leader regions upstream of the V genes. Turquoise and red triangles represent 12RSS and 23RSS, respectively. Constant region exons are represented by green rectangles. (b) Functional variable regions are composed of four conserved structural framework regions (FR) and three more diverse complementarity determining regions (CDR). The CDR3 regions are the most diverse as they span multiple gene segments and contain random nucleotide addition. C) The CDR loops make the most contact with antigen (PDB ID: 1FVC)
