Figure 4. Three Strand Exchange Recombinase Assay.
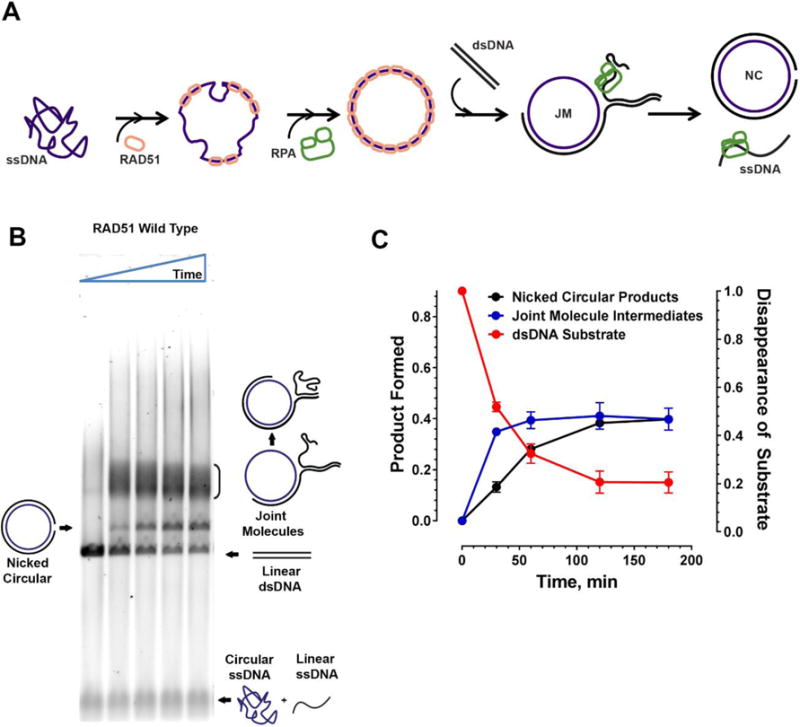
A Active RAD51 nucleoprotein filament is formed on ϕX174 Virion circular ssDNA in reaction conditions permitting ATP hydrolysis followed by addition of RPA which helps remove secondary structures in the ssDNA allowing stable nucleoprotein filament formation. The RAD51 nucleoprotein then invades ϕX174 RFI linear dsDNA to form nicked circular dsDNA products through several joint-molecule intermediates showing various stages of branch migration. The RPA also helps sequester any free displaced ssDNA following strand exchange thereby preventing a reverse reaction. B. Typical agarose gel image from a strand exchange assay used to resolve the substrates, intermediates and the products of the reaction over a time course of 0, 30, 60, 120 and 180 minutes. In reactions containing the wild type protein, nicked circular products can be observed as early as 30 minutes. C. Quantitation of the strand exchange assay gel showing appearance of nicked circular products (black) and joint molecules (blue) on the left Y axis. Disappearance of the linear dsDNA substrate (red) is quantitated on the right Y axis. Time in minutes is indicated on the X axis.
