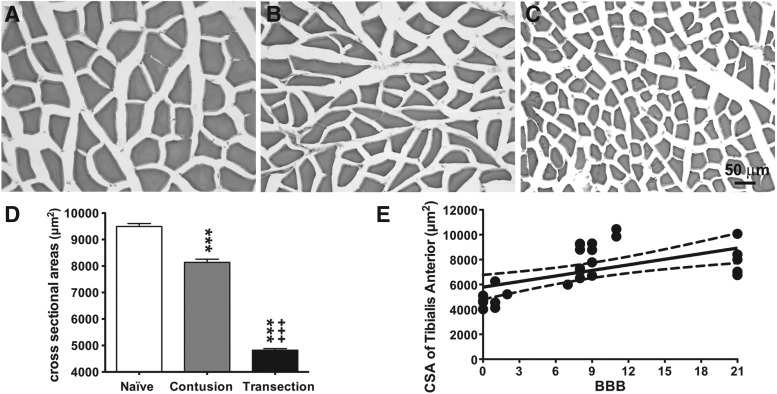
FIG. 5.
Cross-sectional area (CSA) of tibialis anterior myofibers after spinal cord injury ( SC)I. Representative sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin from the naïve group (A), spinal cord contusion group (B), and spinal cord transection group (C) are depicted. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Bar graph showing the effects (mean ± standard error of the mean values) of SCI on the CSA of the tibialis anterior myofibers. CSA was significantly decreased by contusion injury compared with the naïve group. Spinal cord transection resulted in a significantly lower CSA when compared with the contusion group. *** p < 0.005 vs. naïve group; +++ p < 0.005 vs. contusion group; two-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post-hoc for multiple comparisons. (E) Correlation analyses between the Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan (BBB) and average myofiber CSA in the naïve and SCI (contusion and transection) groups. Data are presented as X-Y paired, with linear regression (solid line) and 95% confidence limits (dashed lines) of the fit.