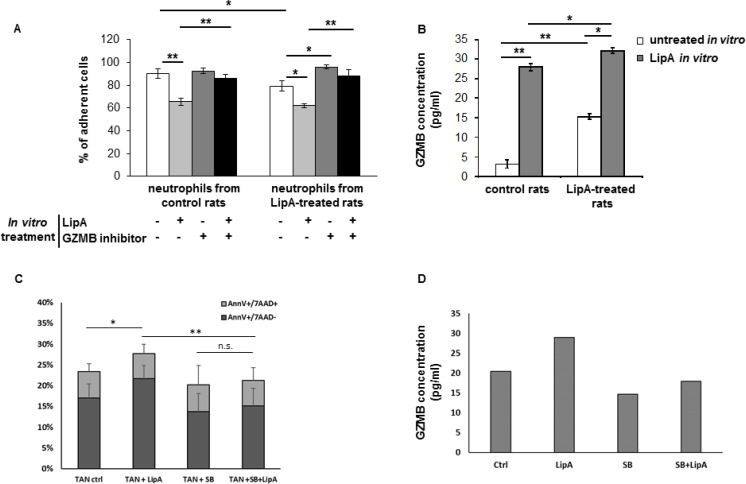
Figure 5. LipA induced neutrophil-mediated cytotoxicity via granzyme B production.
(A, B) Spleen neutrophils from LipA treated or control rats were purified and treated in vitro with or without 10 µg/ml LipA for 24 h. (A) The toxic effect of conditioned media on tumor target cells cultured in the presence or in the absence of GZMB inhibitor was evaluated using a methylene blue assay. The mean numbers of adherent cells are shown as percentages of the untreated cells (100%). (B) The concentration of GZMB in conditioned media was measured by ELISA. Shown are means ± SEM. (C) Neutrophils were incubated or not with LipA (24 h) and stained for granzyme B (green) or DAPI (blue). 3 independent experiments. (C, D) Tumor associated-neutrophils were purified from mice, co-cultures with CT26 cells during 24 h in presence or not of LipA and SB203580. (C) The level of apoptotic tumor cells was determined by Annexin V/7AAD staining. (D) The level of GZMB secreted in co-culture of CT26 and TAN treated or not with LipA and SB203580 was determined using an ELISA assay. The results are obtained from one mouse and are representative of those obtained with at least 6 animals. (A–C) Significant difference in Mann–Whitney U test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n.s. not significant.