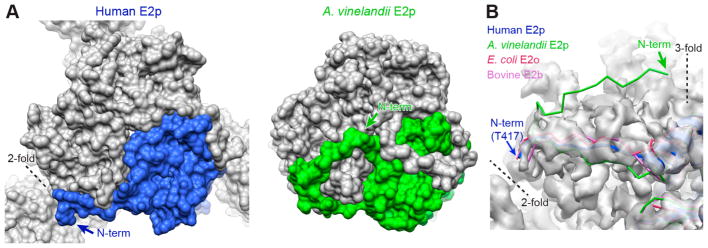
Figure 2.
Position of the N-terminus of the human E2p IC domain. (A) Space-filling models of the IC trimers of human E2p and A. vinelandii E2p, showing how the N-terminal arm of each domain of a trimer extends along an outer edge of a trimer as seen in the 3-fold exterior view. (B) Residues 408–416 of human E2p, corresponding to the region of A. vinelandii E2p structure extending to the 3-fold axis, are not visible in the EM map (transparent gray surface). In contrast to the structure of A. vinelandii E2p, the resolvable N-terminal residues of human E2p, E. coli E2o, and bovine E2b are in similar positions close to the 2-fold axis.