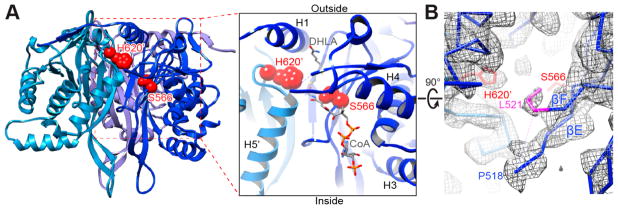
Figure 3.
Interdomain active site of the human E2p IC trimers. (A) One of three active sites in a trimeric unit of human E2p (left) and a close-up view of the active site (right). Three inner domains are shown as ribbons and colored in different shades of blue. The catalytic residues S566 and H620′ from two adjacent IC domains, respectively, are displayed as red spheres. The putative CoA and dihydrolipoamide (DHLA) positions are adopted from A. vinelandii E2p structures (PDB ID: 1EAD and 1EAE). (B) The densities of A519 and G520 are not visible in the EM map (chicken wire) due to their flexibility. The density of the side chain of L521 (colored in purple), whose corresponding residue (L293) in bovine E2b is a gatekeeper residue for binding of the lipoyl group, is well-defined. Only the backbone of the atomic model is shown except for the side chains of L521 and the catalytic residues S566 and H620′.