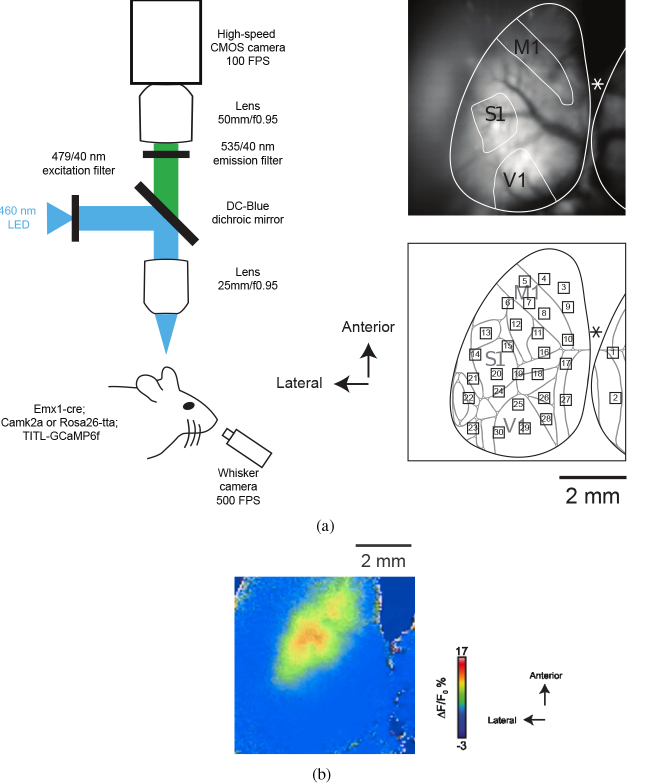
Fig. 2.
a) Left: Illustration of the experimental setup used for widefield imaging of cortical activity of mice expressing GCaMP6f and simultaneous recording of whisker movement. Right, top: raw image of neocortical surface through transparent skull preparation. M1, S1, and V1 are schematically labeled. Asterisk indicates position of Bregma. Right, bottom: ROIs are superimposed on a map based on the Allen Institute common coordinate framework v3 of mouse cortex (brain-map.org; adapted from [43]). ROI: 1, Retrosplenial area, lateral agranular part (RSPagl); 2, Retrosplenial area, dorsal (RSPd); 3, 4, 9, Secondary motor area (MOs); 5, 7, 8, 10, Primary motor area (MOp); 6, Primary somatosensory area, mouth (SSp-m) / upper limb (SSp-ul); 11, 16, Primary somatosensory area, lower limb (SSp-ll); 12, SS-ul; 13, Primary somatosensory area, nose (SSp-n); 14, 20, Primary somatosensory area, barrel field (SSp-bfd); 15, SSp-bfd / Primary somatosensory area, unassigned (SSp-un); 17, Retrosplenial area, lateral agranular part (RSPagl); 18, Anterior visual area (VISa) / Primary somatosensory area, trunk (SSp-tr); 19, VISa / SSp-tr / SSp-bfd; 21, Supplementary somatosensory area (SSs); 22, Auditory area (AUD); 23, Temporal association areas (TEa); 24, SSp-bfd / Rostrolateral visual area (VISrl); 25, 29, 30, Primary visual area (VISp); 26, Anteromedial visual area (VISam); 27, RSPagl / RSPd; 28, Posteromedial visual area (VISpm). b) A sample 20 s movie obtained during a block. Frames corresponding to “AW” are identified by “W”, shown on the top left of frames (see Visualization 1 (932.2KB, mp4) ).