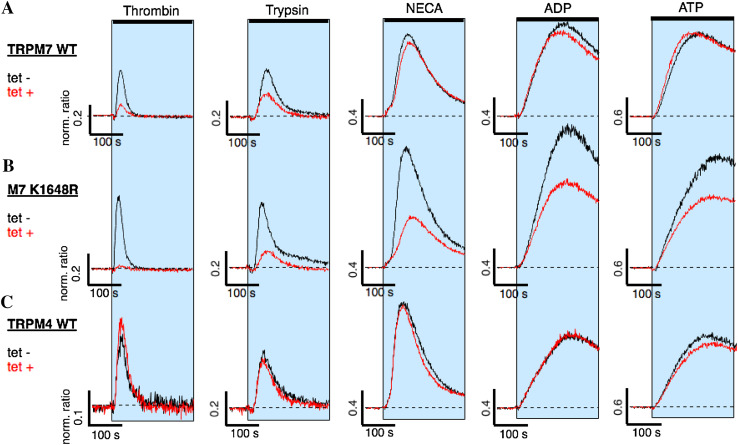
Fig. 4.
Protease- and purinergic receptor-induced Ca2+ release and TRPM7 kinase activity. HEK293-TREx cells overexpressing either human wild-type TRPM7 (TRPM7 WT), a TRPM7 mutant deficient in phosphotransferase activity (M7-K1648R), or human wild-type TRPM4 (TRPM4 WT) were investigated for Ca2+ signals through protease-activated receptor stimulation using thrombin or trypsin, and metabotrophic purinergic-receptor stimulation using NECA, ADP or ATP. Ca2+ release was assessed using a fluorescent kinetic plate reader in the 384-well format (see “Materials and methods”). The 340/380 nm ratio was normalized to 1 to the average of the 10 data points acquired before compound application in each of the 384 wells. The normalized ratio was then plotted against time of the experiment. The shaded areas indicate exposure to the respective agonists in extracellular solution absent of Ca2+: either thrombin (30 U), trypsin (100 nM), NECA (3 mM), ADP (3 mM) or ATP (3 mM) on a hTRPM7-WT (n = 4–8), b hTRPM7-K1648R (n = 4–8), c hTRPM4 (n = 4). Cells were either non-induced (tet-; black line) or induced for 20 h with tetracycline (tet + , red line)