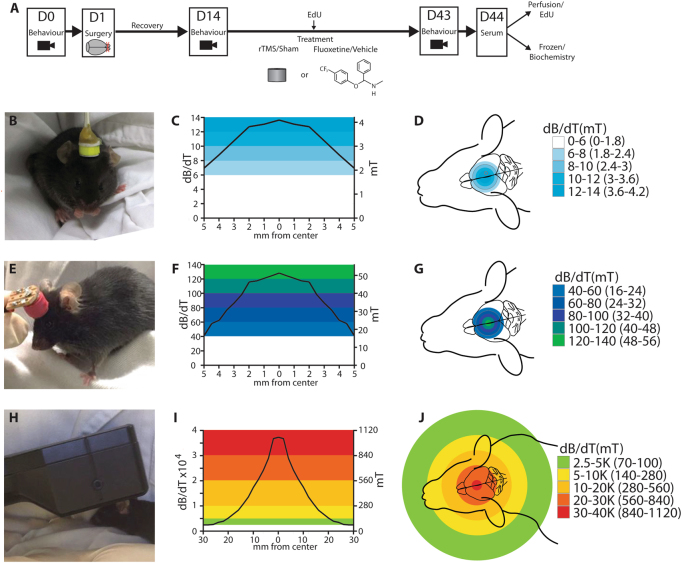
Fig. 1. Overview of experimental design.
a Study design showing timeline and control groups. Study design showing timeline and control groups. Mice received olfactory bulbectomy (OB) or a sham procedure (surgery with olfactory bulbs left intact). Following a 2-week recovery, Mice that had OB underwent 3-min sessions of 10-Hz LI-rTMS (b–d), MI-rTMS (e–g), or HI-rTMS (h–j) 5 days per week over 4 weeks, or received fluoxetine daily (18 mg/kg in cookie dough). Treatment lasted 4 weeks, and some animals received an injection of EdU at the midpoint. Mice underwent behavioral testing before OB, before treatment, and after treatment. Mice were killed humanely at 24 h after the last treatment, and post-mortem serum samples were collected immediately. Brains were prepared for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or EdU histologic evaluation. Behavioral effects were assessed with the forced swim test. Neurobiologic effects were assessed with brain levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and neurogenesis. Peripheral metabolomic changes induced by OB and rTMS were monitored using ELISA and targeted metabolomics driven by ultrapressure liquid chromatography that was evaluated with ingenuity pathway analysis. D day; EdU 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (Thermo Fisher Scientific), rTMS repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Measured magnetic field intensity profiles (in dB/dT and mT) at 2 mm beneath the coil surface (equivalent to cortical surface) for coils used to deliver d low-intensity (LI-rTMS), g medium-intensity (MI-rTMS), and j high-intensity (HI-rTMS). Additional information about magnetic field intensity parameters is provided in supplementary information