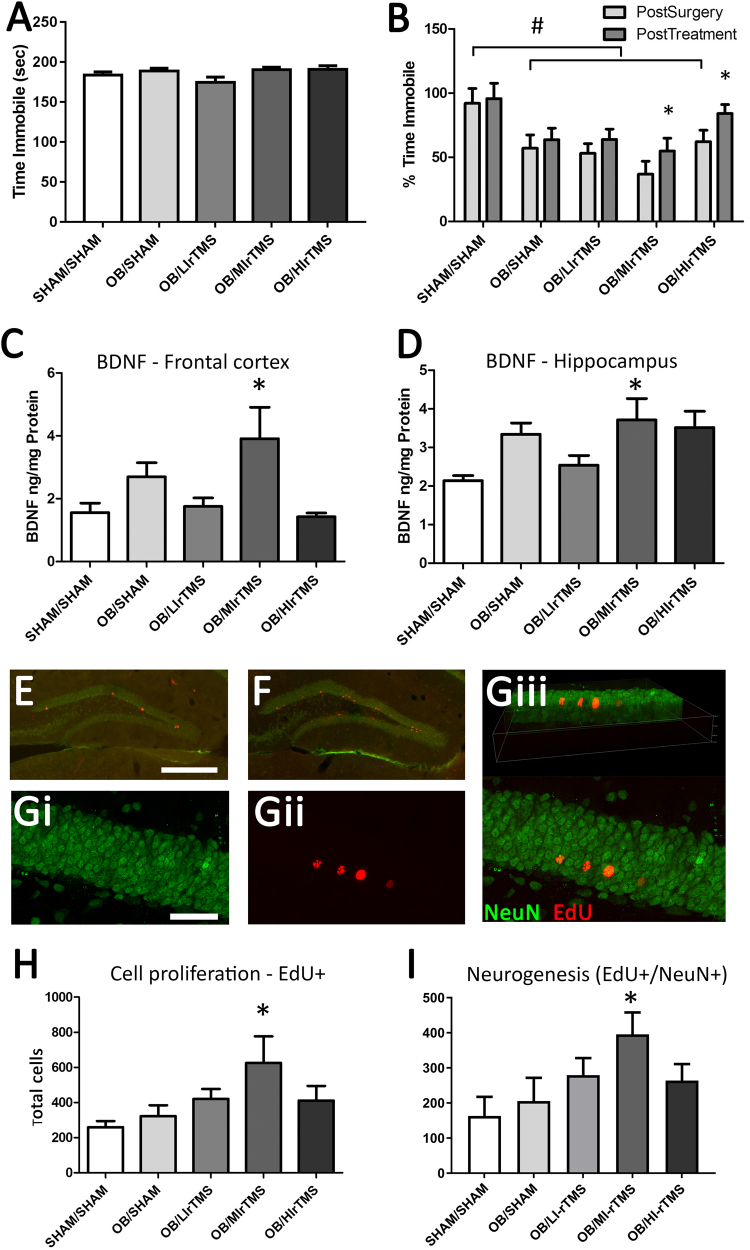
Fig. 3. Comparison of rTMS intensities.
a Time (in seconds) spent immobile at baseline (pre-surgery) for all groups, confirming that there were no differences between animals at the start of the experiment. b Time spent immobile in the forced swim test as a percentage of the pre-surgery value for each animal. OB surgery significantly reduced the time spent immobile compared with pre-surgery values, indicating hyperactivity. Behavior was partially rescued by MI-rTMS treatment. # indicates that post-surgery levels are significantly different from untreated animals. * shows significant differences between post-surgery and post-treatment within a group. c, d BDNF concentration in the frontal cortex (c) and hippocampus (d). Only MI-rTMS resulted in increased BDNF levels compared with sham/sham treatment in both frontal cortex and hippocampus, but no significant differences were observed between any groups compared with OB/sham. * indicates a significant difference compared with sham/sham. e–g Immunohistochemistry showing EdU single-labeled and EdU-NeuN double-labeled cells in the granular and subgranular layers of the dentate gyrus. e, f Low power view of the hippocampus in sham (e) and MI-rTMS (f)-treated mice showing increased Edu labeling following MI-rTMS. confocal microscopy of MI-rTMS-treated animal confirming co-localization of NeuN (gi), EdU (gii), labels merged (giii), with a 3d rotated view showing co-localization of red and green staining within the hippocampal neurons (giii). h, i Number of EdU-positive cells (h) and Edu-NeuN double-labeled cells (i) in hippocampus following OB surgery and rTMS treatment. A significant increase was found in the number of newly born neurons following MI-rTMS compared with OB/sham and sham/sham mice. * shows a significant difference compared with sham/sham and OB/sham. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Scale bars are 500 µm (e) and 50 µm (g). BDNF brain-derived neurotrophic factor, EdU 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (Thermo Fisher Scientific), HI-rTMS high-intensity repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, LI-rTMS light-intensity repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, MI-rTMS medium-intensity repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, NeuN neuron-specific protein, OB olfactory bulbectomy, rTMS repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation