Fig. 8.
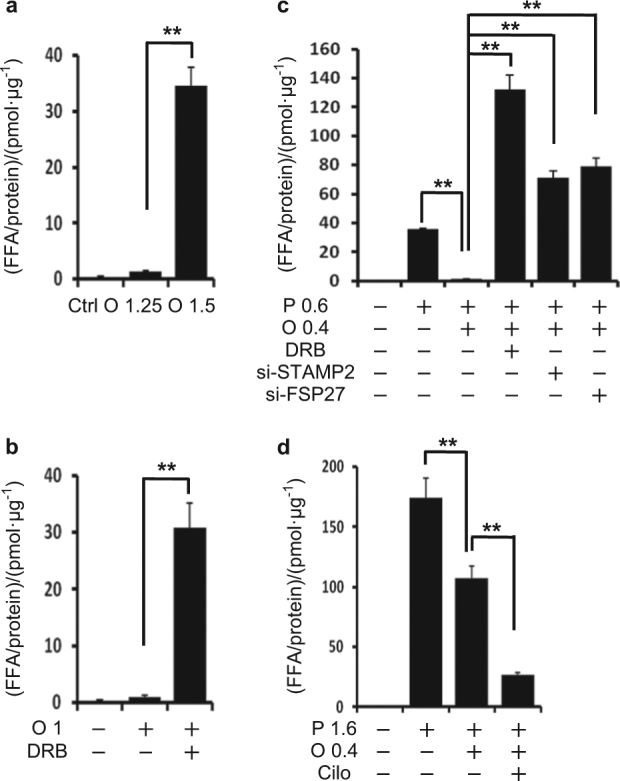
The total cytosolic FFA content is higher in articular chondrocytes that succumb to FFA-induced lipotoxicity than in articular chondrocytes that survive lipotoxicity. a The FFA level in the cytosol of articular chondrocytes treated with 1.25 or 1.5 mmol·L-1 oleate. 1.5 mmol·L-1 oleate significantly increased FFA level in the cytosol compared to experimental control (1 mmol·L-1 oleate). **P < 0.01 vs. experimental control according to Scheffe’s test. b The FFA level in the cytosol of articular chondrocytes treated with 1.0 mmol·L-1 oleate with or without DRB. DRB significantly increased the FFA level in the cytosol. **P < 0.01 vs. experimental control (oleate alone) according to Scheffe’s test. c The FFA level in the cytosol of articular chondrocytes treated with 0.6 mmol·L-1 palmitate with or without 0.4 mmol·L-1 oleate. Oleate supplementation significantly decreased the FFA level in the cytosol of articular chondrocytes treated with 0.6 mmol·L-1 palmitate. DRB, siSTAMP2 and siFSP27 significantly reversed this reduction of FFA level by oleate supplementation (n = 4). **P < 0.01 vs. experimental control according to Scheffe’s test. d The FFA level in the cytosol of articular chondrocytes treated with 1.6 mmol·L-1 palmitate with or without 0.4 mmol·L-1 oleate. Oleate supplementation significantly decreased the FFA level in cells treated with 1.6 mmol·L-1 palmitate. Cilostazol significantly decreased the FFA level in the cytosol of cells co-treated with 1.6 mmol·L-1 palmitate and 0.4 mmol·L-1 oleate (n = 4). **P < 0.01 vs. experimental control according to Scheffe’s test
