Figure 1.
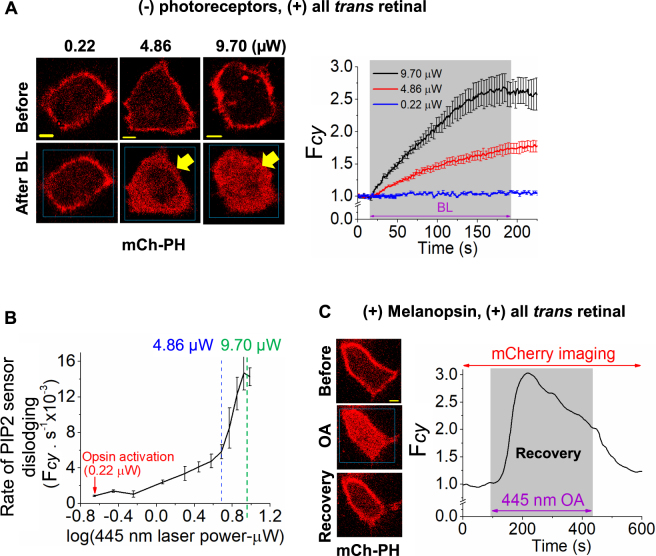
Comparison of photoreceptor dependent PIP2 hydrolysis vs photoreceptor independent PIP2 sensor translocation by photoexcited retinal. (A) Images of HeLa cells incubated with 50 µM ATR (retinal) expressing PIP2 sensor (mCherry-PH). Both images and the plot of Fcy vs time show that cells exposed to 0.22 µW 445 nm blue light did not respond, while cells exposed to 4.86 µW and 9.70 µW blue light exhibited mCherry-PH translocation to cytosol (mean ± S.E.M.). (B) The plot of initial PIP2 sensor dislodging rate vs laser power of 445 nm blue light. (mean ± S.E.M., n = 6 cells in each experiments). (C) Images of HeLa cells expressing Gq-coupled Melanopsin and mCherry-PH. Cells were incubated with ATR (50 µM) for 5 minutes. A significant PIP2 hydrolysis was observed upon optical activation (OA = blue box) of melanopsin using short pulses of blue light (0.22 µW of 445 nm). Recovery of PIP2 sensor to the PM was observed even the blue light exposure is continued. The plot shows the dynamics of PIP2 sensor translocation in cytosol. Mean and S.E.M. are from 3 < independent experiments. (blue light (BL) = blue box). Scale = 5 µm.