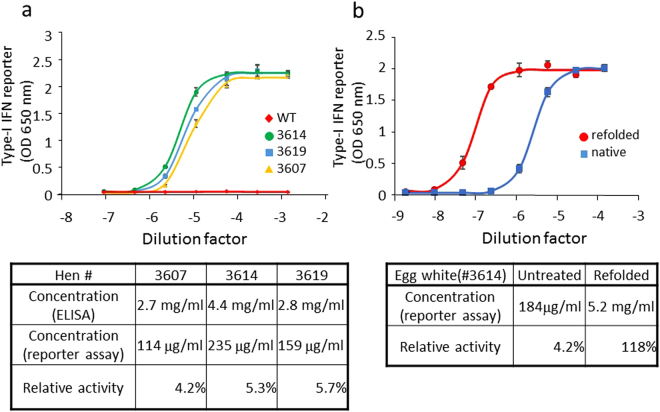
Figure 5.
Detection of bioactive hIFN-β in KI egg white. (a) HEK-Blue IFN-α/β reporter cell samples were individually stimulated with five-fold serial dilutions of egg white from three hIFN-β KI hens (#3607, #3614, #3619) and a WT hen. The cell culture supernatants were assayed for induction of secreted alkaline phosphatase reporter activity using a colorimetric assay. Plots show the mean ± standard deviation values for three independent assays. A four-parameter logistic curve was fit to each dataset, and the EC50 values (median effective concentrations) were calculated for each curve (upper panel). By using the EC50 of a commercially available, purified recombinant hIFN-β as the standard, the absolute IFN-β bioactivities in the KI egg white were calculated [shown as “Concentration (reporter assay)” in the table at the bottom panel]. For comparison, the concentration of hIFN-β in each egg white was determined by ELISA (Fig. 4h), and the relative hIFN-β bioactivities were calculated as the percentage of active hIFN-β in the total amount of IFN-β. (b) Egg white from the hIFN-β KI hen #3614 was denatured in 6 M guanidine hydrochloride and then renatured in the presence of the artificial chaperone, highly polymerized cycloamylose (see Methods). hIFN-β bioactivity in the untreated and renatured egg white was analyzed by the HEK-Blue IFN-α/β reporter assay. Plots show the mean ± standard deviation values for three independent assays. The data are reported as in Fig. 5a.