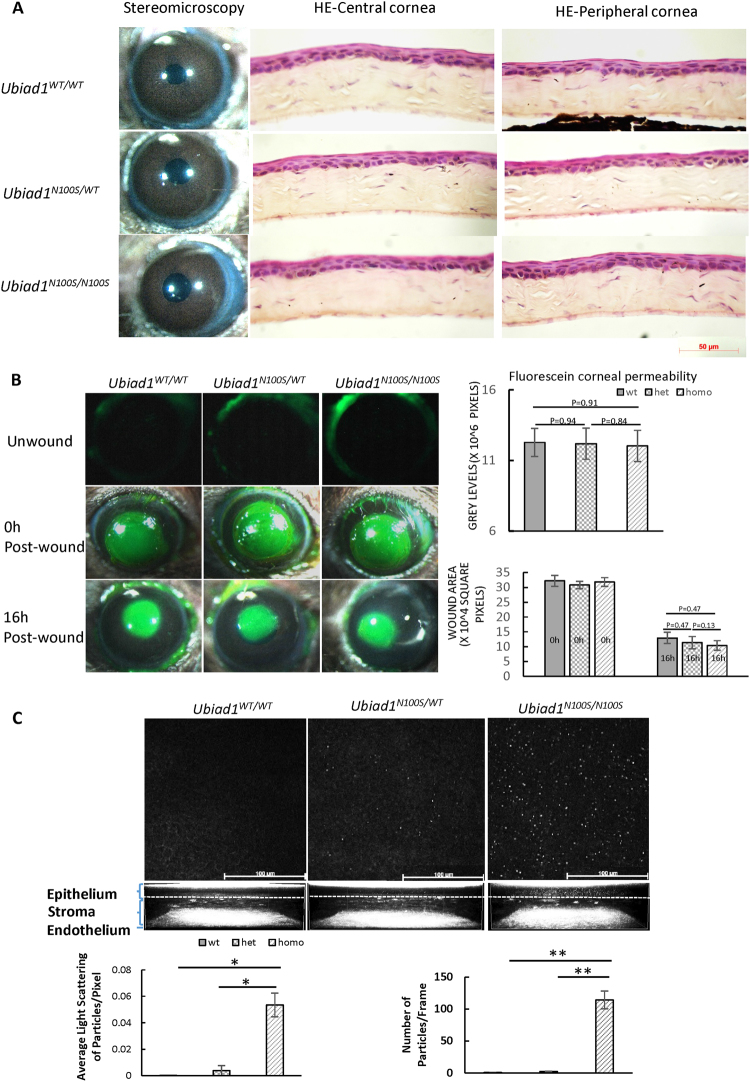
Figure 2.
Minor morphological alterations of the cornea of Ubiad1N100S mice. (A) Stereomicroscopy and H&E staining showed intact and clear cornea and normal cornea morphology for the Ubiad1N100S mutant. Mice were six-month-old of mixed genders. (B) No Corneal epithelial barrier function and wound healing change. Representative images of corneal epithelial fluorescein staining of unwound, 0 h and 16 h after 2 mm debridement wounds of Ubiad1WT/WT, Ubiad1N100S/WT or Ubiad1N100S/N100S mice. Grey levels of the images of unwound cornea revealed no significant difference in corneal epithelial barrier during different genotypes. The average defect remaining in Ubiad1N100S/N100S, Ubiad1N100S/WT and Ubiad1WT/WT mice showed healing of epithelial debridement was similar between three groups. (C) In vivo confocal microscopy analysis of corneal deposits at 6 weeks. Representative extended focus images combined 5 confocal sections of basal epithelium to show the deposits within the cornea. Quantification of corneal deposit light scattering, and particle number was determined as described under the Methods. The two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to analyze the light scattering and particle numbers. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Mice were of mixed genders.