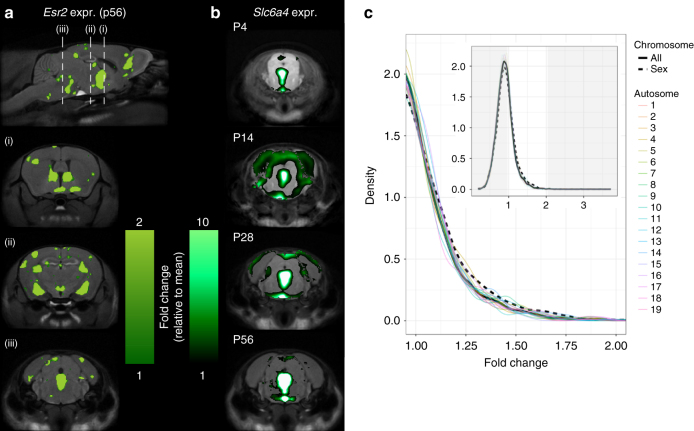
Fig. 7.
Gene expression patterns overlaid onto MRI results. a Spatial Gene Expression of Estrogen Receptor 2 (Esr2) in the adult mouse brain (ABI Dataset ID: 71670737) overlaid onto the MRI average in our study. Esr2 and Esr1 genes (Supplementary Fig. 5) were found to be preferentially expressed in regions with sexually dimorphic development. To measure preferential expression, we used a fold-change measure dividing the mean expression signal in regions with sexually dimorphic development by the mean expression in the brain. Esr2 had fold-change of 2.9 and Esr1 had a fold-change of 2.1. This was primarily driven by expression in Cluster 1, where the genes had fold-changes of 9.9 and 6.1, respectively. b Slc6a4 expression throughout development. Slc6a4 had the highest preferential expression (fold-change of 3.7) in sexually dimorphic regions primarily driven by expression in Cluster 3 (7.0 fold-change). Time course of Slc6a4 gene expression reveals peak expression in mid-brain and hind-brain between p4 and p28. c Genes on sex chromosomes have a higher likelihood of preferential spatial expression in regions with sexually dimorphic development. We computed the fold-change for all the genes in the Allen Brain Atlas and created the density plot marked by the solid line. The dashed line indicates the density plot associated with only the genes on the sex chromosomes and the colored lines represent genes on different chromosomes. In both the overall density plot (inset), and on the zoomed density plot, we see that genes on sex chromosomes have significant preferential expression bias (One-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test: )