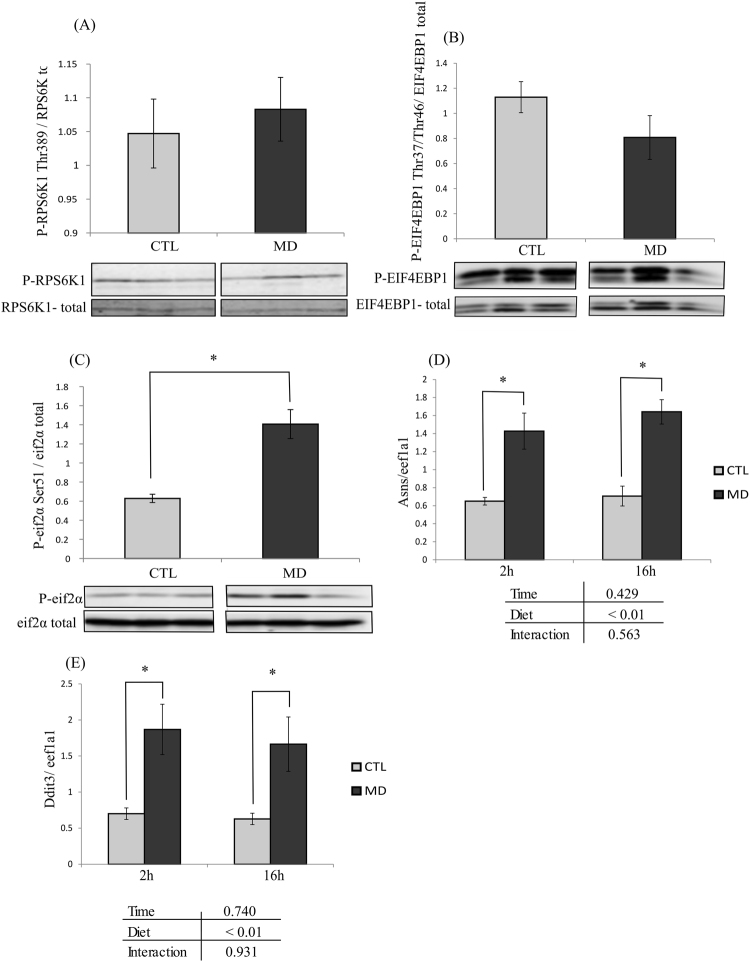
Figure 1.
Effect of methionine deficiency on key factors of the mTOR and GCN2/eIF2α signaling pathways Phosphorylation of (A), ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (RPS6K1) (B) eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 (EIF4EBP1) and (C) eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α) proteins in liver of trout fed the control diet (CTL) or the methionine deficient diet (MD) and sampled 2 h after the last meal. Western blot analysis was carried out on six individual samples per treatment, and a representative blot is shown (Source data for each blot are available in Supplementary Fig. 1). Graphs show the ratio of the amount of the phosphorylated protein: the total amount of the targeted protein. The mRNA levels of (D) asparagine synthetase (asns) and (E) DNA-damage inducible transcript 3 (ddit3) were measured using quantitative real-time RT-qPCR assays in liver 2 and 16 h after the last meal. Expression values are normalized with the eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 α 1 (eef1a1) mRNA. Values are means (n = 6), with standard error of the mean represented by vertical bars. *was used to indicate significant difference between treatment among the two dietary group (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by the student-Newman-Keuls multiple-comparison test).