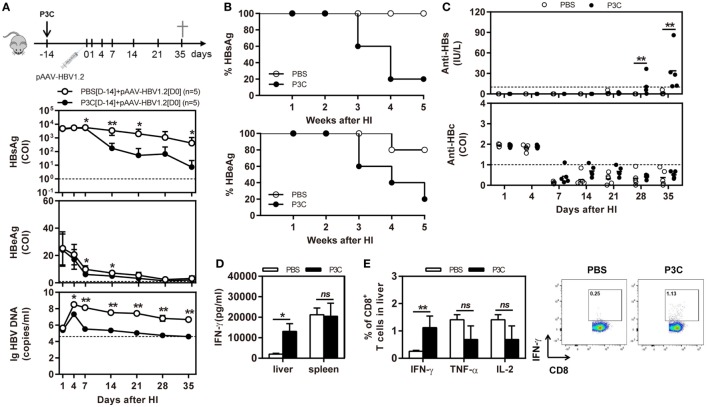
Figure 5.
Pre-treatment with P3C accelerates hepatitis B virus (HBV) clearance in the mouse model for persistent HBV replication and promotes intrahepatic HBV-specific T-cell response. C57BL/6 mice were pretreated once with 20 µg of P3C or phosphate-buffered saline administered by intravenous (IV) injection at day 14 (D-14) before hydrodynamic injection (HI) with plasmid pAAV-HBV1.2. (A) Serological markers of HBV infection HBsAg, Hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg), and HBV DNA were assayed at the indicated time points. (B) Positivity for HBsAg or HBeAg was defined as ≥1*. (C) The serum levels of anti-HBs and anti-HBc antibodies were detected at the indicated time points. (D,E) Lymphocytes were isolated from the mouse liver and spleen at day 35 after HI. (D) The lymphocytes were stimulated with peptide Cor93–100 for 48 h. Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) production was measured by ELISA. (E) The functionality of intrahepatic HBV-specific CD8+ T cells was determined by intracellular cytokine staining after ex vivo stimulation with peptide Cor93–100 for 5 h. The percentage of HBV-specific IFN-γ+ of CD8+ T cells was detected by flow cytometry. Five mice were analyzed per group, and the experiments were repeated at least once. Data were analyzed using an unpaired Student’s t test. Statistically significant differences between the groups are indicated as *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.