Fig. 3.
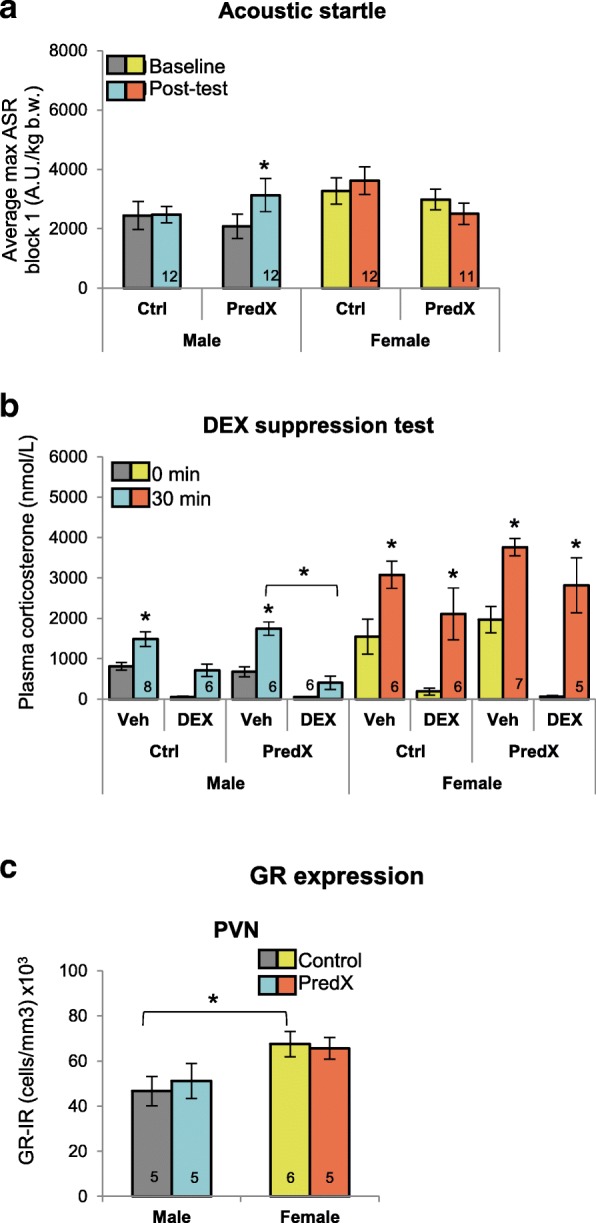
PredX leads to comparable sex differences in ASR and negative feedback control of CORT. a Only males and not females show an enhanced ASR after PredX exposure, replicating the sex difference found after SPS exposure (Fig. 2a). b Likewise, PredX enhanced HPA negative feedback in males but not females. DEX blocked the stress-induced increase in CORT levels only in PredX males, indicating an enhanced sensitivity to DEX in this group and not in PredX females, paralleling results in the SPS model (Fig. 2b). As expected, CORT levels were significantly higher in female compared to males. Again, DEX lowered baseline CORT levels (0 min) to near zero in all groups, demonstrating the effectiveness of DEX in both sexes. c Unlike SPS, PredX did not affect GR expression in the PVN of either sex, although the baseline sex difference was replicated (see Fig. 2c); females have more GR+ neurons in the PVN than males. These data suggest that GR expression in the PVN may be responsive to only some types of stress. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Significance set at P < .05 (indicated by asterisk) for planned pairwise comparisons (Bonferroni). Refer to Additional file 2 for full statistical results
