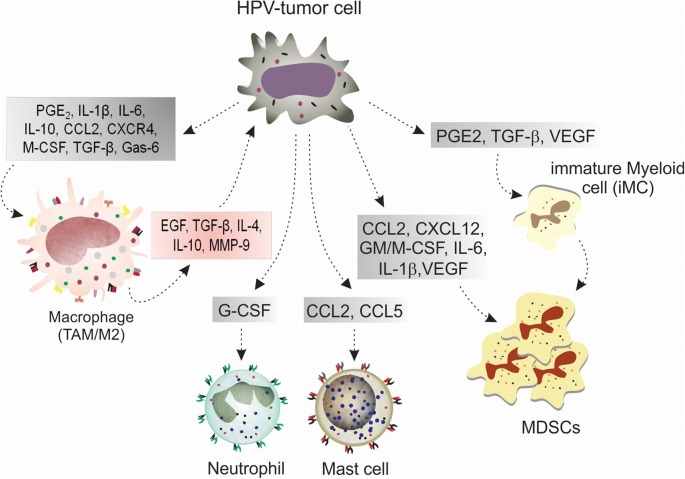
Fig. 3.
Cross-talk between tumor, MDSCs and immune cells for development of HPV-related carcinogenesis. As demonstrated in the figure and in the text, HPV-tumor cell plays a central role in HPV-related carcinogenesis. This cell is able to secret a number of proinflammatory and immunosuppressive factors, which induce macrophage differentiation towards M2 phenotype, iMC differentiation towards MDSCs as well as the recruitment and activation of both MDSCs and proinflammatory immune cells (macrophages, neutrophils and mast cells). Major molecules for the occurrence of these events are: CCL2 and CXCL12, for cell recruitment; TGF-β, IL-1β and IL-10, for immunosuppression; MMP-9, for tumor invasion; and STAT3, due to the activation of JAK/STAT3 intracellular signalling pathway which enables the occurrence of cell response to all stimuli caused by the engagement of the shown cytokines and factors to their respective receptors