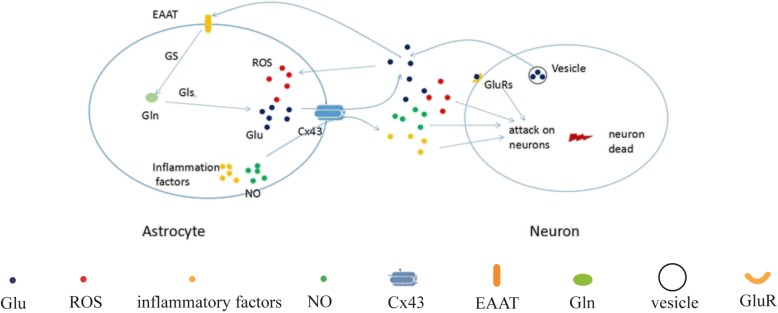
Fig. 7.
Function and regulation of connexin 43 in astrocyte-neuron co-cultures. The attack of ischemia results in massive vesicular release of glutamate from neurons. The astrocyte glutamate transporter, EAAT, transport extracelluar glutamate into the cell, downregulate extracellular glutamate level. The glutamate entering astrocytes were synthesized to glutamine under the catalysis of glutamine synthetase, which can be hydrolysis to glutamate by the action of glutaminase. After the attack of ischemia, the expression and function of EAAT is decreased, resulted in reduced glutamate clearance; excessive glutamate promotes the production of ROS; meanwhile, astrocyte stimulation produce inflammatory factors, all of them cause neuronal death.
Cx43, connexin 43; EAAT, excitatory amino acid transporter; NO, nitric oxide synthase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Gls,glutaminase; GluRs, glutamate receptors; GS, glutamine synthetase; Gln, glutamine; Glu, glutamate.