Fig. 1A.
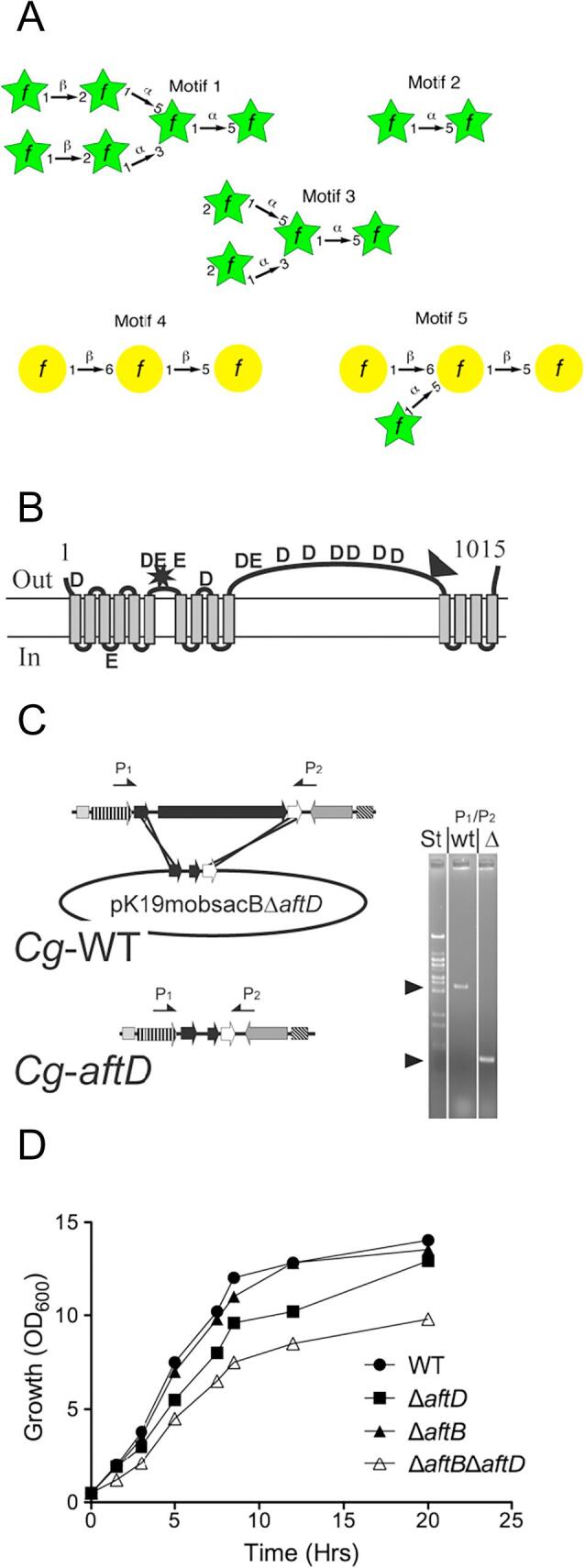
Common glycosyl linkage motifs found within mycobacteria and corynebacteria (A), topology of AftD (B), knock out strategy (C) and effect on growth in liquid media (D). A, The hexaarabinosyl (motif) 1 is the site of mycolic acid esterification, the [α-D-Araf(1 → 5]-α-D-Araf (motif 2) represents the main linear segments of D-arabinan, the [α-D-Araf(1 → ]3,5-α-D-Araf (motif 2) illustrates the main bifurcation points of a single D-arabinan chain, and motifs 4 and 5 show the linkage profiles of linear D-galactan configuration of how D-arabinan is attached to D-galactan. B, topology of C. glutamicum AftD with the black triangle indicating the location of the 388 aa insertion in the M. tuberculosis ortholog of AftD. The topology prediction is based on the dense alignment surface method. The conserved aspartyl and glutamyl residues are indicated as D and E, respectively. The star indicates the two catalytic motifs resembling those of glycosyltransferases of the GT-C family (Liu and Mushegian, 2003). C, strategy to construct C. glutamicumΔaftD. Shown is the wild type genomic aftD-region and the deletion vector pK19mobsacBΔaftD carrying 18 nucleotides of the 5′-end of aftD and 36 nucleotides of its 3′-end thereby enabling the in-frame deletion of almost the entire Cg-aftD gene. Selection for homologous recombination results in C. glutamicumΔaftD (Cg-aftD). The arrows marked P1 and P2 locate the primers used for the PCR analysis to confirm the absence of Cg-aftD. Distances are not drawn to scale. The results of the PCR analysis are shown on the right, where the amplification product obtained from the wild type (WT) and that of the deletion mutant of (Δ) was marked accordingly. The sizes of 4032 bp for the wild type and of 1051 bp for the deletion mutant were as expected and marked by an arrow head. St marks the standard. D, the consequences of Cg-aftD deletion and Cg-aftB/Cg-aftD double deletion on growth in rich medium (BHI). Growth of C. glutamicum (●), C. glutamicumΔaftD (■), C. glutamicumΔaftD (▲) and C. glutamicumΔaftBΔaftD (Δ).
