Fig. 1. Human RA synovial fluid is rich in AnxA1-positive neutrophil MVs that protect cartilage.
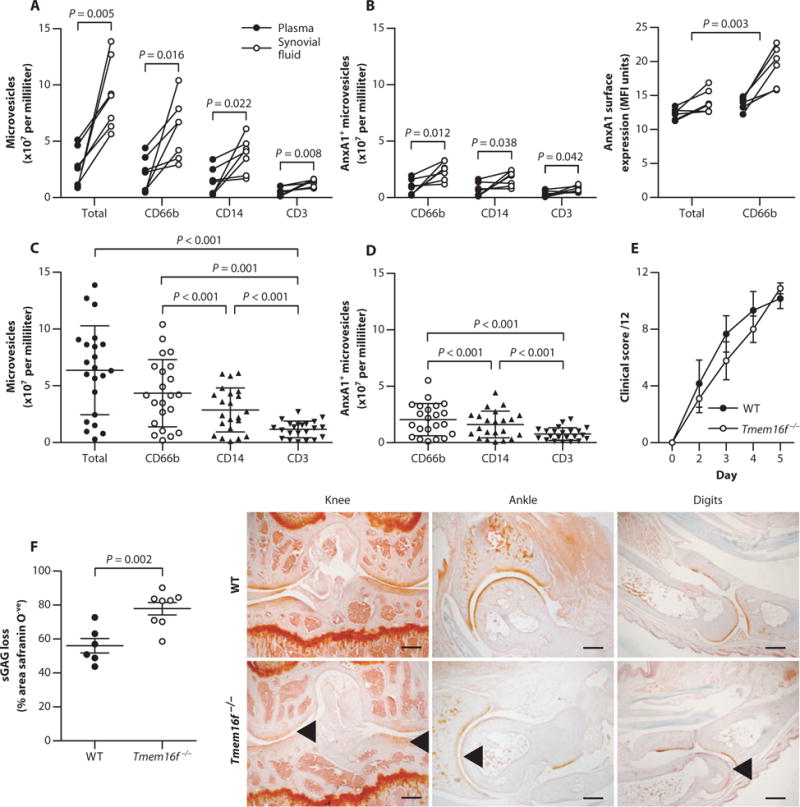
(A and B) CD66b, CD14, and CD3 expression on MVs (A) and the presence and expression levels of AnxA1-positive MVs (B) from paired synovial fluid and plasma of RA patients (n = 7). P values were determined by paired, two-tailed Student’s t test. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (C and D) Validation of synovial MV phenotype (C) and AnxA1+ MVs (D) in additional RA patient synovial fluid samples (n = 22). Data are means ± SD. P values were determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni multiple comparison test. (E) Mice deficient in the putative phospholipid scramblase TMEM16F (Tmem16f−/−) and wild-type (WT) littermate controls were administered K/BxN serum to induce arthritis. Clinical scores are means of all joints ± SEM (n = 9 Tmem16f−/− and 6 WT mice). (F) Sections from digits, wrists, ankles, and knees at day 5 from mice in (E) were assessed for sGAG loss by safranin O staining. Data are means ± SEM (n = 6 to 9). P value was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. Arrowheads indicate sGAG loss. Scale bars, 250 μm.
