Fig. 6. Neutrophil MVs protect from cartilage degradation in models of inflammatory arthritis.
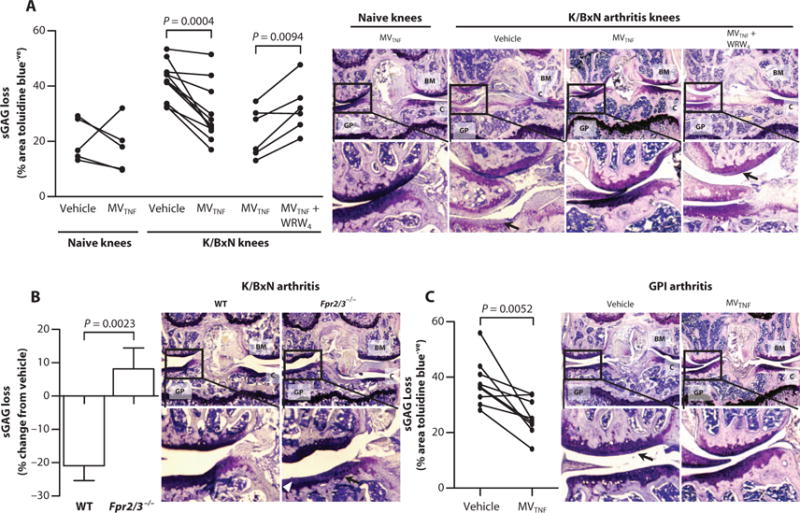
(A and B) Mice received arthritogenic K/BxN serum (100 μl) on days 0 and 2; on day 3, vehicle (left knee; PBS, 5 μl) or MVTNF (right knee; 3 × 104 in 5 μl) with or without WRW4 (10 μM) was injected intra-articularly into WT (A) or Fpr2/3−/− mice (B). On day 5, knee joints were sectioned and stained with toluidine blue for sGAG content, and representative images are shown; black arrows in (A) indicate sGAG loss, and white arrowheads in (B) indicate cartilage surface fibrillations. Data are calculated from three sections per paired knees with three images per section (n = 5 to 9). P values were determined by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA and Bonferroni posttest. (C) DBA-1 female mice (n = 9) were immunized with GPI peptide on day 0 and administered vehicle intra-articularly in the left knee (PBS, 5 μl) or MVTNF in the right knee (3 × 104 in 5 μl) intra-articularly on day 21. Knee joint sections were stained with toluidine blue, and representative images are shown; black arrows indicate sGAG loss. Data are from three sections per knee with three 20× images captured per section. P values were determined by paired, two-tailed Student’s t test. In (A) to (C): BM, bone marrow; GP, growth plate; C, cartilage.
