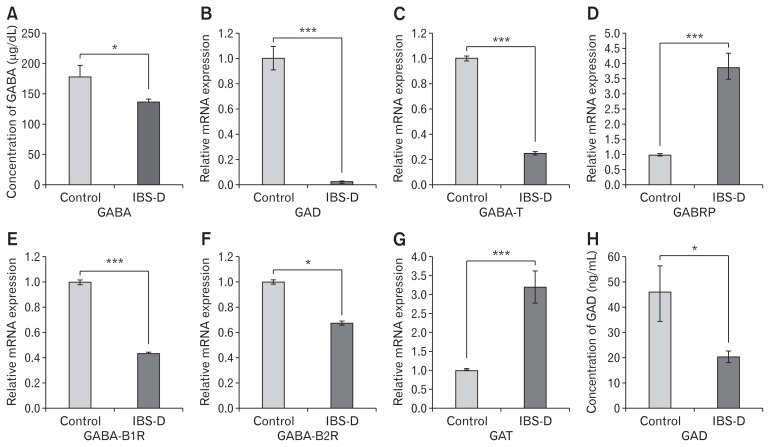
Figure 1.
Quantification of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in serum and analysis of expression of GABAergic signal system in colon biopsy samples of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) patients and controls. (A) Concentration of GABA in human serum samples measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), control (n = 28) and IBS-D (n = 25). Relative mRNA expression of (B) glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). (C) GABA-transaminase (GABA-T). (D) π subunit of GABA-A receptor (GABRP). (E) B1 subunit of GABA-B receptor (GABA-B1R). (F) B2 subunit of GABA-B receptor (GABA-B2R). (G). GABA-transporter (GAT) in control (n = 20–25) and IBS-D (n = 20–23) determined through reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. (H). Concentration of GAD in serum samples measured by ELISA, (n = 20–25). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and were examined with Student’s paired t tests. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 was considered to be significant.