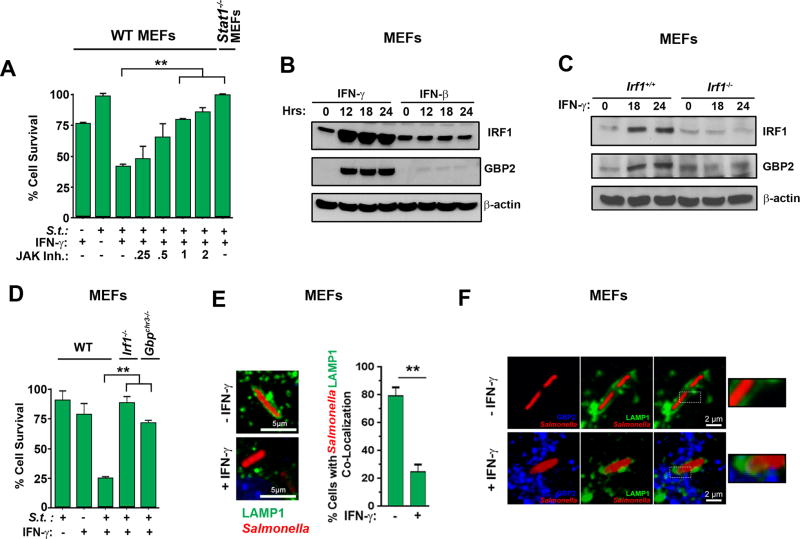
Figure 3. IFN-γ sensitizes Salmonella-infected non-phagocytic cells to death via Jak/STAT1-mediated induction of IRF1 and GBPs.
(A) Viability of wild-type MEFs infected with Salmonella (MOI 10) and treated with IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) in the presence of increasing amounts of JAK inhibitor I. Viability of stat1−/− MEFs infected with Salmonella (MOI 10) and treated with IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) is also shown (rightmost bar). (B) Wild-type MEFs treated with IFN-γ or IFN-β (10ng/ml each) for the indicated times were examined for IRF1 and GBP2 by immunoblotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. (C) Irf1+/+ and irf1−/− MEFs were treated with IFN-γ (10ng/ml) for the indicated times and examined for IRF1 and GBP2 by immunoblotting. (D) Wild-type, irf1−/− and gbpchr3−/− MEFs were infected with Salmonella (MOI 10) in the presence or absence of subsequent IFN-γ treatment (10ng/ml) and cell viability was determined 48 h.p.i. (E) Wild-type MEFs stably expressing LAMP1-GFP were infected with Salmonella-RFP in the presence or absence of IFN-γ (10ng/ml), and localization of LAMP1-GFP and Salmonella-RFP was determined by confocal microscopy. Representative images of co-localization (left) and quantification of cells showing co-localized Salmonella with LAMP1-GFP, indicative of intact SCVs (right) are shown. (F) Wild-type MEFs stably expressing LAMP1-GFP were infected with Salmonella-RFP and subsequently treated with IFN-γ (10ng/ml). Localization of Salmonella (red), LAMP1 (green) and GBP2 (blue) was determined by confocal microscopy. Enlarged images of boxed sections are shown to the right. Note that LAMP1-GFP encapsulates Salmonella in the absence of IFN-γ. Upon IFN-γ treatment, LAMP1-GFP encapsulation is lost and GBP2-LAMP1-Salmonella co-localization becomes evident. Viability data shown in this figure are representative of at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent mean +− SD. **p<0.005.