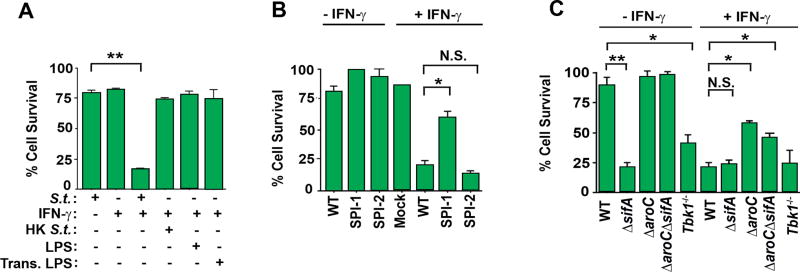
Figure 4. Induction of cell death requires live Salmonella in the cytosol.
(A) Wild-type MEFs were infected with Salmonella (MOI 10), heat-killed Salmonella (MOI 10), treated with LPS (4 ng/ml), or transfected with LPS (4 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of IFN-γ (10ng/ml) and cell viability was determined 48 h.p.i. (B) Wild-type MEFs infected with either wild-type Salmonella (MOI 10), Salmonella lacking its first pathogenicity island (ΔSPI-1), or its second pathogenicity island (ΔSPI-2) were exposed to IFN-γ (10ng/ml) and cell viability was determined 48 h.p.i. (C) Wild-type MEFs were infected with either wild-type Salmonella (MOI 10), Salmonella lacking sifA (ΔsifA) (MOI 10), aroC (ΔaroC) or both sifA and aroC (ΔsifAΔaroC) (MOI 10), exposed to IFN-γ (10ng/ml), and cell viability was determined 48 h.p.i. In parallel, MEFs lacking tbk1 were infected with Salmonella (MOI 10) and exposed to IFN-γ (10ng/ml); cell viability was determined 48 h.p.i. Viability data shown in this figure are representative of at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent mean +− SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.005