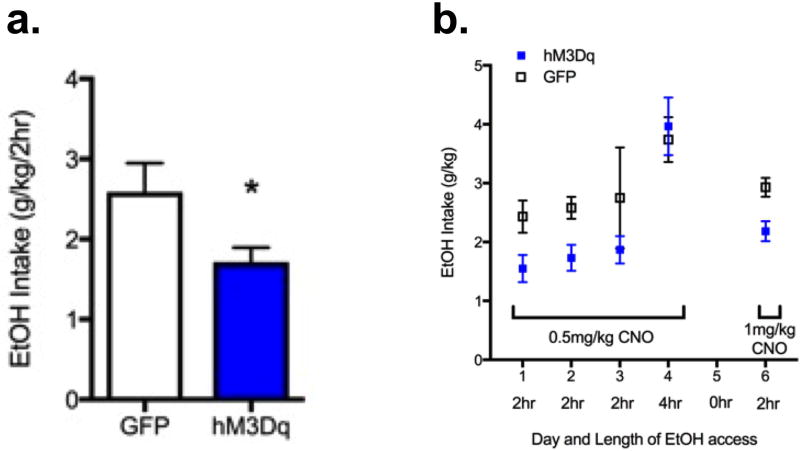
Figure 2. Increasing NAc core and shell activity decreased acute binge-like ethanol drinking.
a) Average 2 hr intake for individuals on DID days 1,2,3: Mann-Whitney test, Median ethanol intake for GFP and hM3Dq mice were 2.33g/kg (n=8) and 1.79 g/kg (n=7); the distributions in the two groups differed significantly (Mann–Whitney U = 7, p = 0.01, two-tailed). b) Increasing NAc core+shell activity decreased acute binge-like ethanol drinking on Days 1,2,3 and 6. Two way ANOVA (only includes data from 2 hr drinking days 1, 2, 3, and 6) revealed main effect of AAV group F(1,52)=9.70, p < 0.01). The effect of CNO on mice expressing hM3Dq was noticeably absent on day 4, when ethanol access was 4 hr. There was not a significant difference in intake between 0.5 and 1 mg/kg CNO. Because the half-life of CNO is ~2 hours, the length of access to ethanol drinking was adjusted to 2 hours in subsequent studies. n=7–8/group.