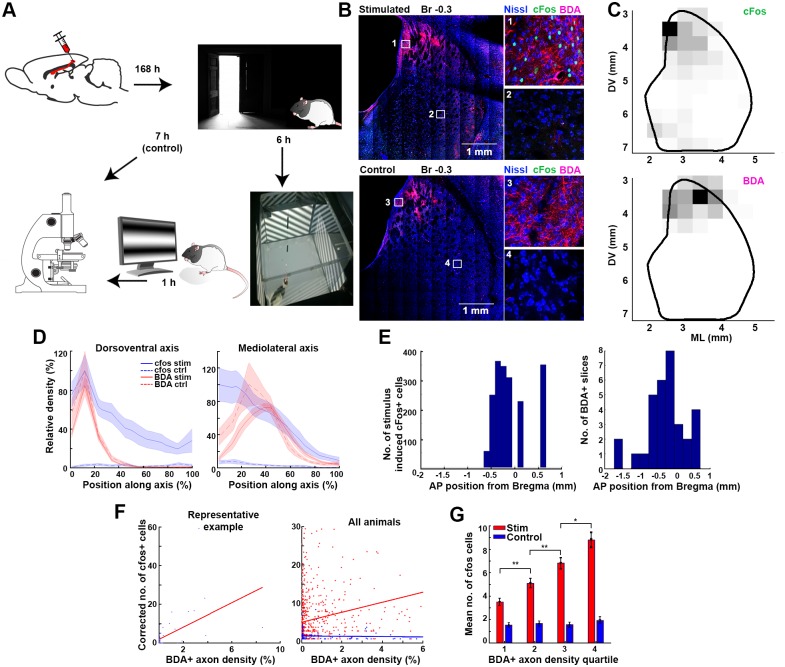
Fig 2. Colocalization of the stimulus-induced striatal cFos expression and the axon terminals from the visual cortex.
(A) Experimental schematics. (B) Representative example sections of a visually stimulated (upper panels) and a control animal (lower panels). Blue, red, and green color channels are assigned to the respective fluorochromes of the Fluoro Nissl, BDA, and cFos immunohistochemistries. Insets show the magnified areas marked by rectangles on the left panels. Note the lack of cFos+ neurons on the lower (control) panels, while the anterograde BDA tract tracing from the visual cortex shows a similar axonal distribution pattern in both cases. (C) Unsupervised quantification of the striatal distribution of cFos+ neurons (top panel) and BDA+ axons (bottom panel) in a representative coronal section of a stimulated animal’s brain. See also S1 Fig. (D) cFos (blue) and BDA (red) density distribution in stimulated (solid lines) and control animals (striped lines). Left and right panels show the distributions along the respective DV and ML axes of the striatum. (E) AP distribution of visual stimulation—induced cFos+ somata (left panel) and the distribution of slices with detectable FluoroGold-labeled axons (N = 37 slices in 9 animals). Note that the BDA+ axons target the similar AP segment of the CPu where the visually inducible cFos activity was present. (F) Correlation of the normalized cFos and BDA densities in a representative stimulated animal (left panel) and in all animals (right panel). The right and blue dots of the right panel and regression lines, respectively, represent data from the stimulated and sham animals. (G) Mean number of the cFos+ neurons in the striatum calculated for the 4 BDA axon density quartiles. Note that while the higher BDA density predicts higher cFos+ cell numbers in the stimulated animals (red), the cFos+ density is constant with no respect to the BDA distribution in the control animals (blue). AP, anteroposterior; BDA, biotinylated dextran amine; CPu, caudate putamen; DV, dorsoventral; ML, mediolateral.