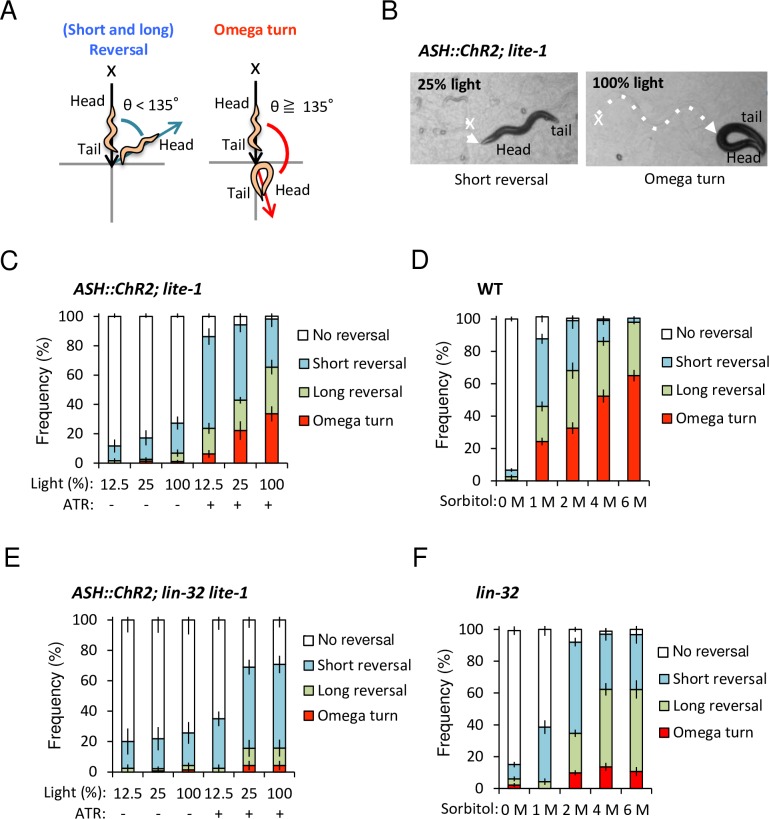
Fig 1. lin-32 is required for proper optimization of probability of omega turn with proportional stimulus strength.
(A) A scheme of the avoidance behaviors [11]. After contacting a noxious stimulus (x), an animal exhibits backward behavior. Short and long reversal are subdivided by the backward length with 1~2 head swings or three head swings or greater without omega turn, respectively. An omega turn is specifically defined by reorientation angles (θ ≧135) following the backward behaviors with/without either short reversal or long reversal. (B) lite-1 mutants expressing ChR2(H134R) in ASH sensory neurons (ASH::ChR2(H134R); lite-1) exhibit short reversal (left panel, dashed line) with 25% light irradiation (x) and omega turns (right panel, dashed line) with 100% light irradiation (x). (C) ASH::ChR2(H134R); lite-1 animals with ATR can optimize their dominant behaviors from reversals to omega turns with proportional to light intensity. n = 6,7,9,8,7,11. (D) Wild type animals adjust probability of omega turns depending on the sorbitol drop concentration. n = 17,30,20,20,20. (E) ASH::ChR2(H134R); lin-32 lite-1 animals showed reduced omega turns even with ATR and 100% light intensity. n = 4,7,7,4,7,7. (F) lin-32 animals show reduced omega turns independent on the sorbitol drop concentration. n = 20,7,33,20,12. n = plate (cohort) of approximately 10–20 animals. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM.