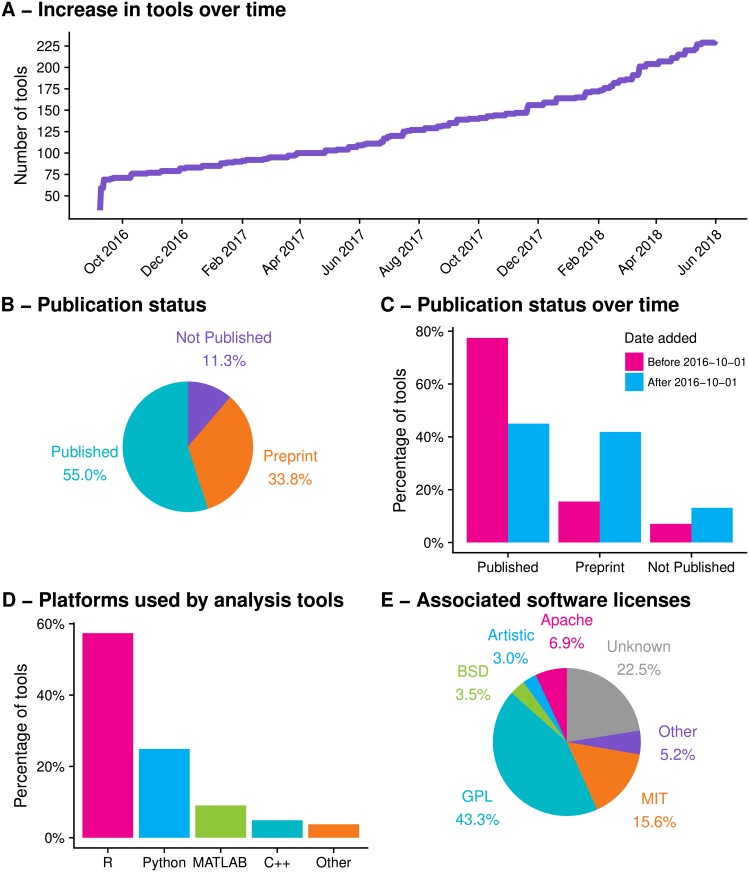
Fig 1.
(A) Number of tools in the scRNA-tools database over time. Since the scRNA-seq tools database was started in September 2016 more than 160 new tools have been released. (B) Publication status of tools in the scRNA-tools database. Over half of the tools in the full database have at least one published peer-revirew paper while another third are described in preprints. (C) When stratified by the date tools were added to the database we see that the majority of tools added before October 2016 are published, while around half of newer tools are available only as preprints. Newer tools are also more likely to be unpublished in any form. (D) The majority of tools are available using either the R or Python programming languages. (E) Most tools are released under a standard open-source software license, with variants of the GNU Public License (GPL) being the most common. However licenses could not be found for a large proportion of tools. Up-to-date versions of these plots (with the exception of C) are available on the analysis page of the scRNA-tools website (https://www.scrna-tools.org/analysis).