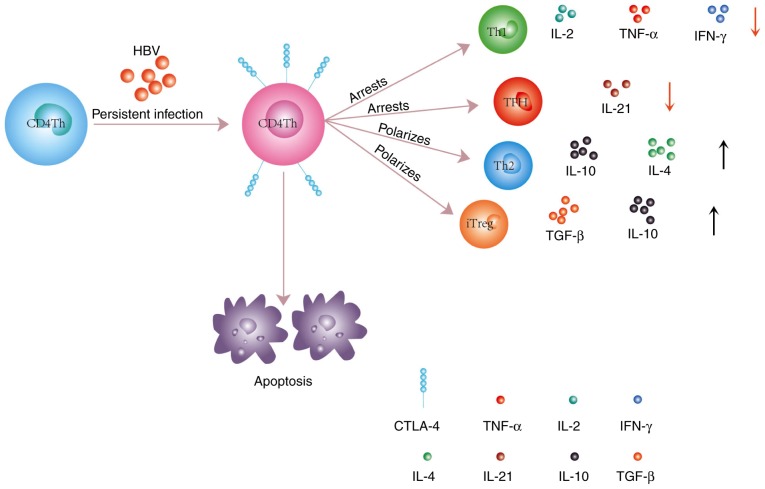
Figure 2.
CD4+ Th cells have similar susceptibility to apoptosis to CD8+ T cells following persistent HBV infection. Upregulated expression of CTLA-4 on CD4+ Th cells polarizes them toward the Th2 and iTreg phenotypes, which results in an increase of anti-inflammatory cytokine (TGF-β, IL-10, and IL-4) levels. Conversely, the differentiation of proinflammatory cells, such as Th1, TFH and CD4+ Th cells, is blocked, and the levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-21, and IFN-γ) is decreased. Th, T helper cells; HBV, hepatitis B virus; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; iTreg, peripherally-inducible Treg; TGF, transforming growth factor; IL, interleukin; TFH, follicular helper T cells; IFN, interferon.