Table 4.
Parameter estimates for HLM analysis examining Compulsive Internet Use as function of time (treatment effect) moderated by compliance
| Compulsive Internet Use | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Model 0 | Model 1 | Model 2 | |
| Fixed effects | ||||
| Initial status | Intercept (γ00) | 28.24 | 35.45 | 30.80 |
| (1.39) | (2.35) | (2.88) | ||
| p < .001 | p < .001 | p < .001 | ||
| Compliance (γ01) | 11.07 | |||
| (4.41) | ||||
| p = .016 | ||||
| Rate of change | Slope (γ10) | −3.94 | −1.84 | |
| (1.10) | (1.33) | |||
| p = .001 | ||||
| Compliance (γ11) | −5.09 | |||
| (2.06) | ||||
| p = .018 | ||||
| Variance components | ||||
| Level 1 | Within-person (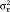 ) ) |
86.49 | 66.59 | 64.58 |
| (14.97) | (16.86) | (15.86) | ||
| p < .001 | p < .001 | p < .001 | ||
| Level 2 | Initial status (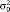 ) ) |
49.66 | 61.31 | 35.67 |
| (18.69) | (64.90) | (57.58) | ||
| p = .008 | ||||
Rate of change (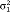 ) ) |
5.74 | 0.58 | ||
| (13.74) | (12.13) | |||
| Covariance (σ01) | −6.97 | 4.54 | ||
| (27.43) | (24.08) | |||
| Model fit parameters | ||||
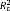 |
.23 | .25 | ||
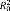 |
.42 | |||
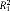 |
.90 | |||
| −2 log-likelihood | 834.10 | 820.56 | 814.21 | |
| AIC | 840.10 | 832.56 | 830.21 | |
Note. Standard errors are displayed in parentheses. The rate of change displays the amount of change per observation. 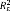 : estimates the proportion of explained within-person variation (level 1);
: estimates the proportion of explained within-person variation (level 1); 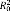 : estimates the proportion of explained between-person variation in the intercept (level 2);
: estimates the proportion of explained between-person variation in the intercept (level 2); 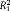 : estimates the proportion of explained between-person variation in the slope (level 2); HLM: hierarchical linear models; AIC: Akaike’s information criterion.
: estimates the proportion of explained between-person variation in the slope (level 2); HLM: hierarchical linear models; AIC: Akaike’s information criterion.
