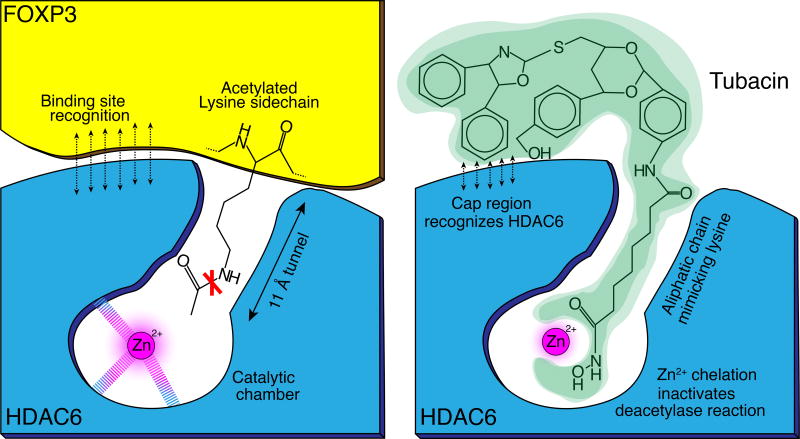
Figure 3. HDAC6 inhibitor design.
Schematic representation of how HDAC6 deacetylates Foxp3 and how this process can be inhibited with an HDAC6 inhibitor, e.g. Tubacin. The aliphatic lysine sidechain fits into a tunnel, leading to a catalytic chamber containing a zinc ion that is essential for the deacetylation reaction. HDAC inhibitors take advantage of this principle and are designed to mimic the aliphatic lysine side chain to fit into the tunnel. Instead of an acetyl group, the HDAC6 inhibitor has a zinc binding group, chelating the Zn2+ ion and blocking the deacetylation reaction. HDAC-isoform specificity is achieved through the ‘cap region’ of the molecule fitting to the surrounding amino acid side chains specific to HDAC6.