Figure 1.
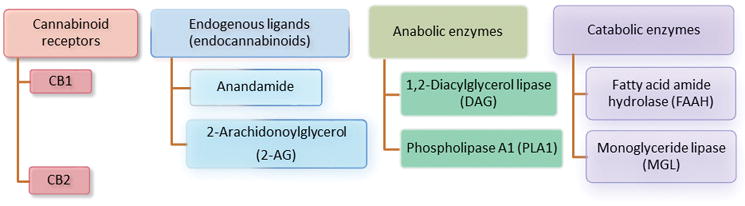
Components of the endogenous cannabinoid system. The cannabinoid (CB) receptors CB1 and CB2 belong to the G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily, coupled to Gi/o proteins and, under certain conditions, coupled to Gs. CB1 receptors are expressed mainly in the brain and CB2 are expressed mostly in the peripheral immune system and in the CNS in the hippocampal CA2/3 pyramidal neurons and glial cells. The endocannabinoid system also includes two arachidonic acid derivatives ligands (anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol) [1], two enzymes responsible for synthesizing endogenous ligands (1,2-diacylglcerol lipase and phospholipase A), and two enzymes responsible for the metabolism of endogenous ligands (fatty acid amide hydrolase and monoglyceride lipase).
