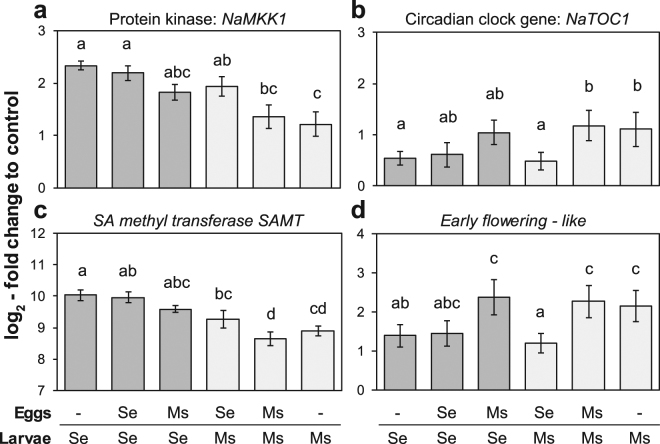
Figure 7.
N. attenuata genes shifted by oviposition in their species-specific feeding-induced expression. In plants fed by either S. exigua (Se, dark bars) or M. sexta (Ms, light bars) larvae, transcript accumulation (mean ± SEM) of (a) the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (NaMKK1: Na_454_10210), (b) a SA methyl transferase (SAMT: Na_454_08320), (c) the circadian clock gene timing of CAB expression (NaTOC1: Na_454_09895), and (d) an early flowering-like gene (Na_454_09170) was determined by real-time qPCR and normalized to EF1α as reference gene and expressed relative to untreated control plants. Plants were previously oviposited by either of the two species or not (−) and letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 according to linear mixed-effects models with the different herbivory treatments as fixed factors and replicate block as random factor followed by a Tukey post-hoc test (N = 9–10).