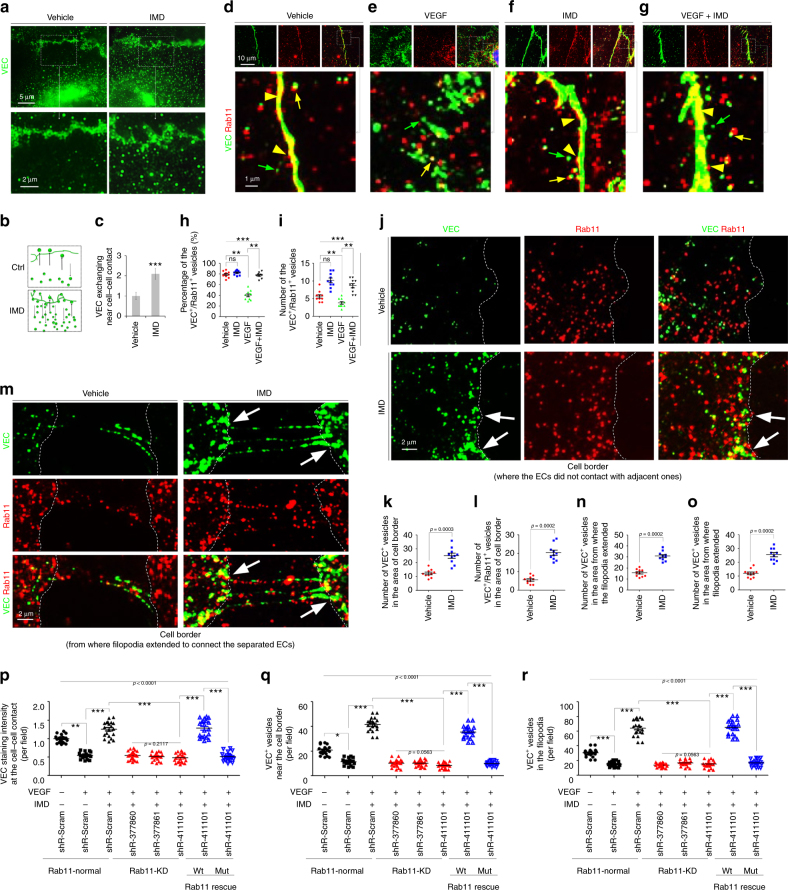
Fig. 2.
Rab11 facilitates the IMD-induced VEC re-localization. a The HUVECs treated with vehicle (PBS) or IMD40 (2 μM) were stained with VEC (green). b The schematic of the VEC endosome exchange at the cell–cell contact. c The VEC exchange was quantified using 10 randomly chosen fields from two experiments and expressed relative to the vehicle group. d–g The Antibody feeding assay was performed as described in Methods. The HUVEC monolayer was treated with PBS, IMD, VEGF, or VEGF plus IMD. The internalized VEC endosomes were detected by pre-incubation of anti-VEC (green), and double-stained with anti-Rab11 (red). The yellow arrows indicate the VEC+/Rab11+ double-positive vesicles, the yellow arrowheads indicate the Rab11+ vesicles fused to the VEC-complexes, and the green arrows indicate the VEC+ endosomes that did not co-localized with Rab11. h, i The percentage of VEC+/Rab11+ vesicles in total VEC+ vesicles and the absolute number of them were quantified using 10 randomly chosen fields. j, m The Antibody feeding assay showed the VEC+ and Rab11+ vesicles at the cell border of HUVECs. k, l, n, o The number of VEC+ or VEC+/Rab11+ double-positive vesicles in the area of cell border where cells did not contact with adjacent ones (k,l), or the area from where the filopodia extended to connect the separated ECs (n, o) were quantified using 10 randomly chosen fields. p, q, r The HUVECs were transfected with the shRNAs of Rab11 (shR-377860, shR-377861, shR-411101), followed by the treatment of VEGF with or without IMD40. shR-411101 that targets the 3′-UTR of Rab11 was rescued by transfecting the vector that expresses wild type or mutant Rab11 lacking 3′-UTR. The VEC staining intensity at the cell–cell contact, and the VEC+ vesicles at the cell border and in the filopodia were quantified using 10 randomly chosen field. All data were presented as scatter plots with mean ± SEM. Significance was assessed by Mann–Whitney test (c, k, l, n, o) and Kruskal–Wallis test followed by non-parametric Dunn’s post-hoc analysis (p–r)