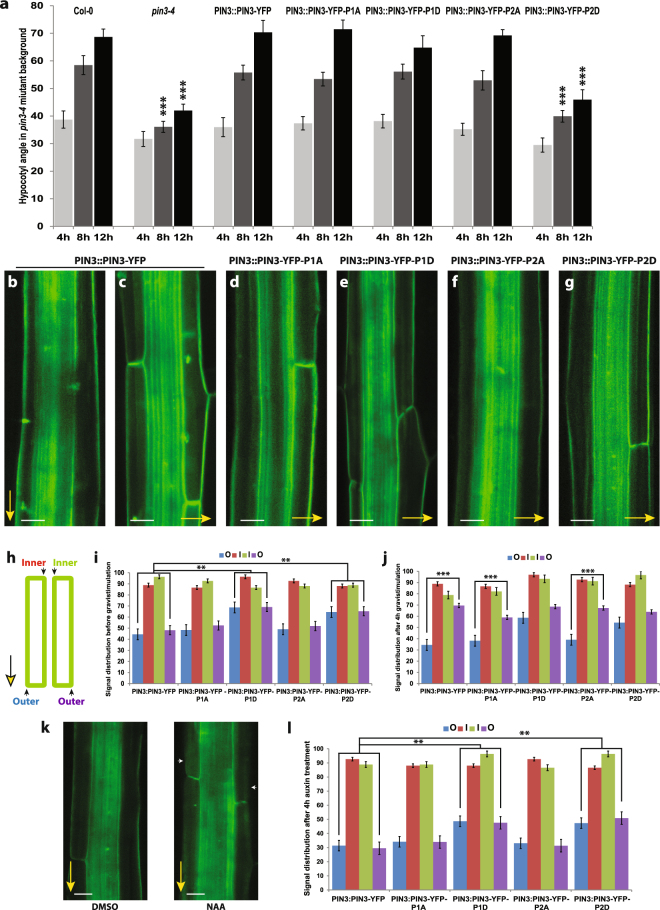
Figure 5.
PIN3 phosphorylation is required for PIN3 polarization and hypocotyl gravitropic response. (a) Hypocotyl bending kinetics of PIN3 mutant variants during gravitropic response. Curvatures were measured every 4 hours. Student’s T-test was calculated for the comparison of each line with the control (Col-0). PIN3-P2D mutant variant shows slower hypocotyl bending. (b–g) Localization of PIN3-YFP before and after 4 hours of gravistimulation (b,c) and after gravistimulation in PIN3-YFP-P1A (d), PIN3-YFP-P1D (e), PIN3-YFP-P2A (f), and PIN3-YFP-P2D (g). Yellow arrows indicate gravity vector. (h) Scheme of quantification showing measured membranes in hypocotyl. (i) Quantification of PIN3 signal distribution in hypocotyl endodermal cells. Student’s T-test was calculated for the comparison of outer membranes signal within each line. PIN3-P1D and PIN3-P2D exhibit higher signal intensity on outer-lateral membranes. (j) Quantitative evaluation of gravity-dependent PIN3 relocation in hypocotyl endodermal cells. Student’s T-test was calculated for the comparison of outer membranes signal within each line. Both PIN3-P1D and PIN3-P2D show defective gravity-induced PIN3-YFP relocation. (k) Localization of PIN3-YFP before and after 4 hours of 10 μM NAA treatment in wild type. White arrows indicate depletion of PIN3 protein from outer-lateral cell membranes. (l) Quantification of PIN3-YFP signal in endodermal cells of hypocotyl after 4 hours of 10 μM NAA treatment. Student’s T-test was calculated for the comparison of each line with the control (PIN3::PIN3-YFP). PIN3-P1D and PIN3-P2D exhibit reduced auxin-induced PIN3 inner-lateralization. Error bars represent SE, (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). Yellow arrows indicate gravity vector. Bars = 10 µm.