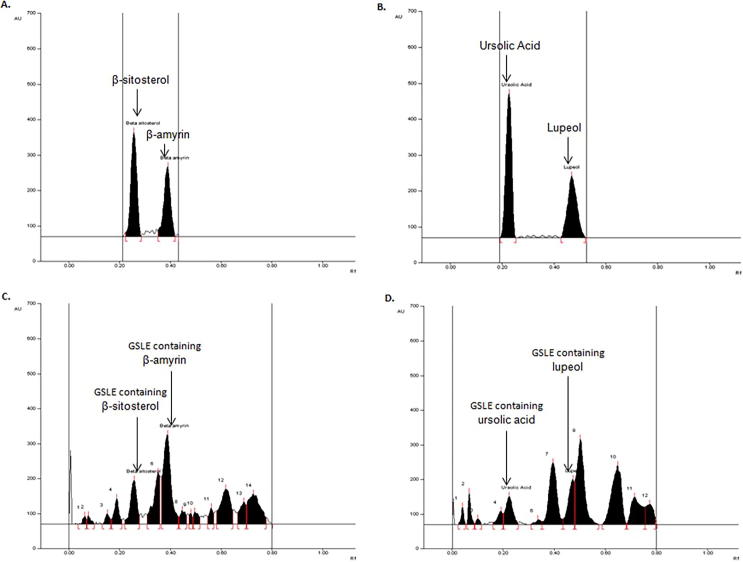
Fig. 5.
Chromatograms of antioxidant biomarkers analysis in GSLE. (A) Chromatogram of β-sitosterol (Rf = 0.25) and β-amyrin (Rf = 0.39) scanned at λmax = 540 nm; mobile phase (Method I) - hexane: ethylacetate (7.5: 2.5; v/v). (B) Chromatogram of ursolic acid (Rf = 0.23) and lupeol (Rf = 0.47) scanned at λmax = 630 nm; mobile phase (Method II) – chloroform: methanol (97:3; v/v). (C) Chromatogram of GSLE (β-sitosterol, spot 5, Rf = 0.25; β-amyrin, spot 7, Rf = 0.39) scanned at λmax = 540 nm; mobile phase (Method I) – hexane: ethylacetate (7.5: 2.5; v/v). (D) Chromatogram of GSLE (ursolic acid, spot 5, Rf = 0.23; lupeol, spot 8, Rf = 0.47) scanned at λmax = 630 nm; mobile phase (Method II) - chloroform: methanol (97:3; v/v).