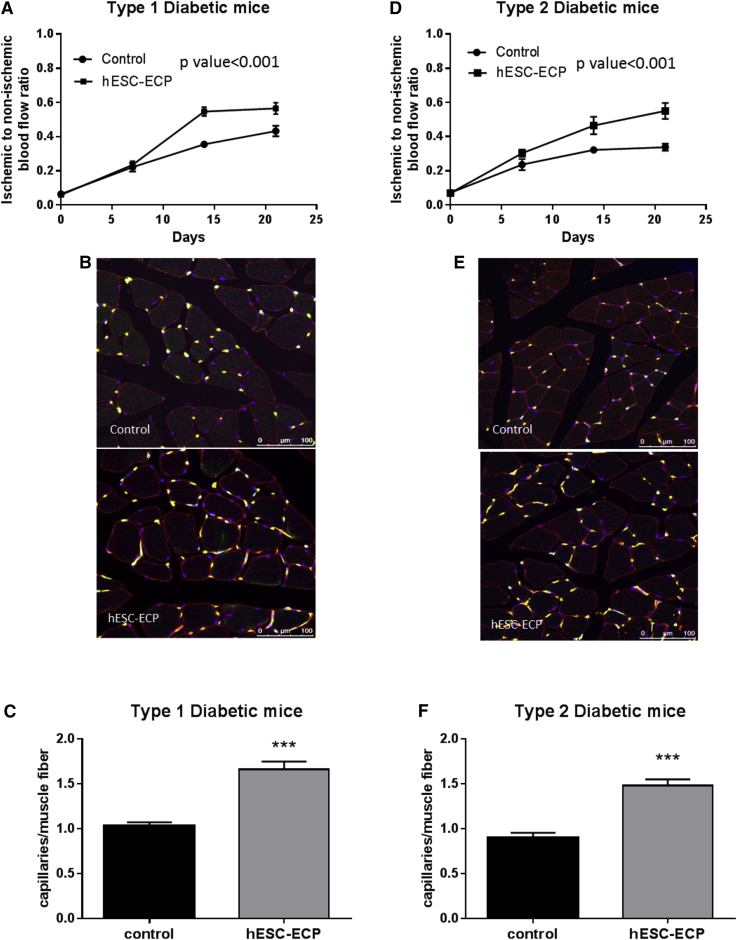
Figure 6.
hESC-ECP Significantly Increase Post-ischemic Blood Flow Recovery in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetic Mice
Foot perfusion was assessed following hindlimb ischemia in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type 1 diabetic CD1 mice and in BKS.Cg-Dock7m+/+LeprdbJ (db/db) type 2 diabetic mice treated with either vehicle (EBM-2; control) or hESC-ECP. Blood flow recovery was expressed as the ratio of ischemic to contralateral blood flow at 0, 7, 14, and 21 days post-treatment for (A) STZ-induced type 1 diabetic mice and (D) db/db type 2 diabetic mice, n = 12, p < 0.001, correlated outcome analysis. Representative images demonstrating endothelial cell (green), muscle (wheat germ agglutinin; red), and nuclear (DAPI; blue) markers in control (top) and hESC-ECP-treated (bottom) adductor muscles from (B) STZ-induced type 1 diabetic mice and (E) db/db type 2 diabetic mice are shown. Scale bar indicates 100 μm. (C) Capillary density expressed as the ratio of capillaries/muscle fiber in STZ-induced type 1 diabetic mice, n = 7, p < 0.001, and (F) db/db type 2 diabetic mice, n = 8, p < 0.001, Mann Whitney U test, is shown. All data represent mean ± SEM.