Figure 1.
Cardiac Cell Therapy Using PSC-CMs
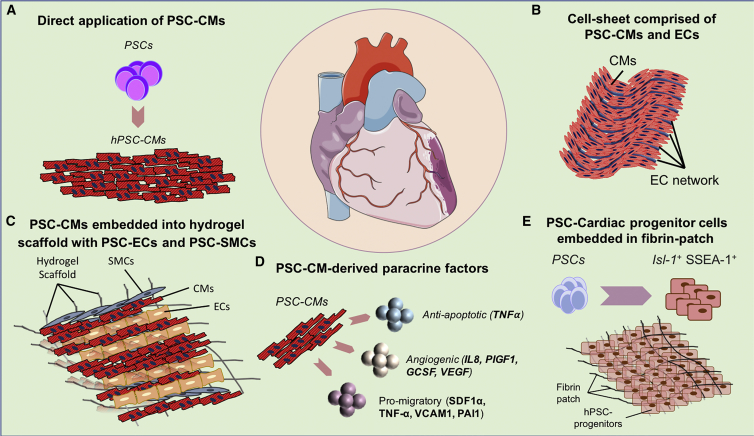
Illustration of recent cell therapy approaches to recover lost cardiac muscle following severe myocardial injury. (A) As alternatives to direct injection of PSC-CMs in the injured heart, (B) tissue engineering approaches have been employed to increase the survival and functional engraftment of cells following delivery. (C) The integration of endothelial cells forming vascular networks into PSC-CM cell sheets facilitates delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the graft, greatly augmenting its engraftment and function as a novel contractile unit. Providing a structural framework with hydrogel and other cell types complementary to CMs such as ECs and smooth muscle cells may boost functional integration into the host myocardium. (D) The secretion of growth factors and cytokines represents another way that administered PSC-CMs might benefit cardiac performance following injury. (E) Finally, the use of scaffolds formulated from fibrin patches containing PSC-derived cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs) is another therapeutic application. PSCs, pluripotent stem cells; PSC-CMs, PSC-derived cardiomyocytes; ECs, endothelial cells; SMCs, smooth muscle cells; Isl-1, Islet-1; SSEA-1, stage-specific embryonic antigen-1.