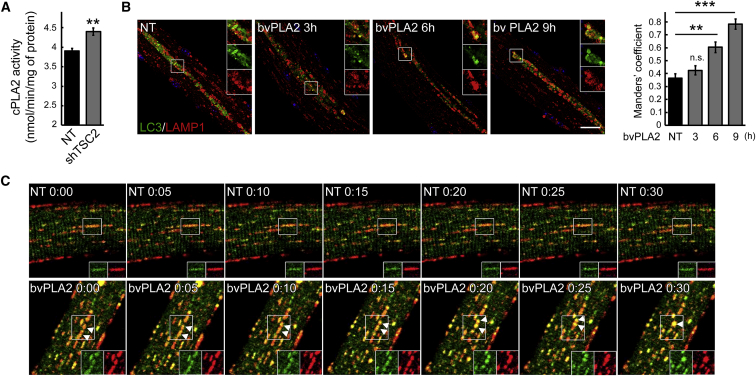
Figure 4.
A Putative Role for PLA2 in the Resorption of Autophagic Buildup
(A) Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) activity was increased in KO muscle following TSC knockdown. The activity was measured in muscle lysates from untreated (NT) and AAV-shTSC-infected (shTSC2) KO mice (n = 4 for each condition). (B) Bee venom PLA2 (10 μg/mL) stimulated lysosomal-autophagosomal fusion in KO muscle fibers. Cultured live fibers were isolated from FDB muscle derived from GFP-LC3:KO mice; the fibers were incubated with PLA2 for 3, 6, or 9 hr, followed by fixation and staining with anti-LAMP1 antibody. Improved lysosomal-autophagosomal fusion is indicated by a significant time-dependent increase in the number of LAMP1/MAP1LC3a-positive structures. (n = 4 for NT; n = 7 for 3 hr; n = 10 for 5 hr; n = 3 for 9 hr). Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Time-lapse confocal microscopy of live muscle fibers cultured in the presence of PLA2 showing a gradual increase in the lysosomal-autophagosomal fusion. FDB muscles from GFP-LC3:KO mice were in vivo transfected by electroporation with plasmid containing mCherry-LAMP1. Images were taken on a Carl Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope with a 20× objective. Graphs represent mean ± SE. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Student’s t test.