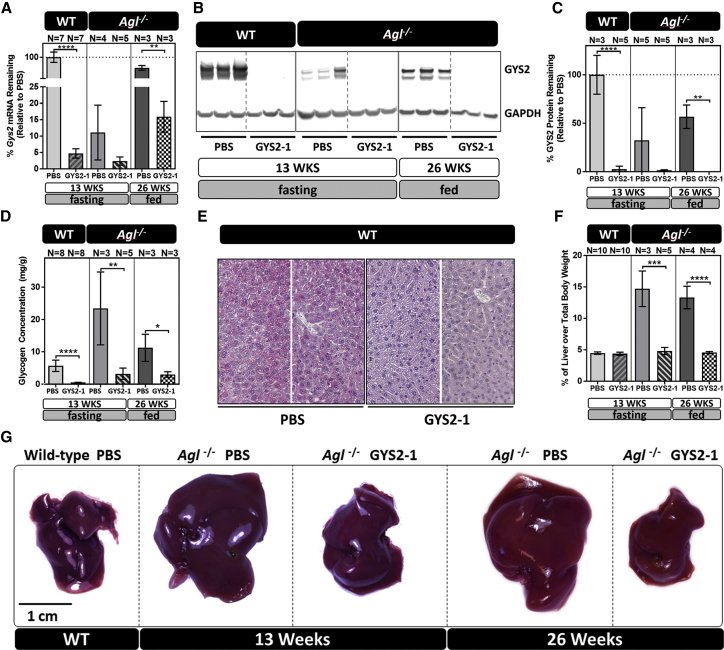
Figure 2.
GYS2-1 Treatment Reduces Gys2 mRNA, GYS2 Protein Expression, Glycogen Synthesis, and Hepatomegaly in GSD III, Agl−/− Mice
The lead Gys2 siRNA conjugate, GYS2-1, was subcutaneously injected into WT and Agl−/− mice at a 10 mg/kg dose. Wild-type and Agl−/− mice were given 10 weekly doses of GYS2-1 starting at 4 weeks of age and sacrificed at 13 weeks of age after a 6-hr fast. In a second experiment, Agl−/− mice were given 18 weekly doses of GYS2-1 starting at 8 weeks of age and sacrificed at 26 weeks of age. Liver samples were collected 24 hr following the final dose. (A) Results of RT-PCR analysis on the effect of GYS2-1 on Gys2 mRNA expression in both wild-type (****p < 0.0001) and Agl−/− (**p ≤ 0.01) mice are shown. (B and C) Western blot analysis (B) and quantification (C) to measure GYS2 protein expression in both wild-type (p < 0.0001) and Agl−/− (**p ≤ 0.01) mice treated with GYS2-1 is shown. (D) Measurement of glycogen in prepared liver extracts in wild-type (p < 0.0001) and Agl−/− (**p ≤ 0.01 for 13 weeks and *p ≤ 0.05 for 26 weeks) mice treated with GYS2-1. (E) Detection of glycogen levels in formalin-fixed liver tissues in wild-type mice using PAS staining. (F) Liver to body weight ratio was measured in Agl−/− mice (***p ≤ 0.001 for 13 weeks and ****p < 0.0001 for 26 weeks) treated with GYS2-1. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Unpaired t test for statistical significance relative to PBS treatment group at each time point. (G) Representative images of livers from each group as indicated. The scale bar represents 1 cm. WT, wild-type littermate.