Figure 6. FIGURE 6: An antagonism between 53BP1-RIF1 and BRCA1-CtIP regulates DSB repair pathway choice in mammalian cells.
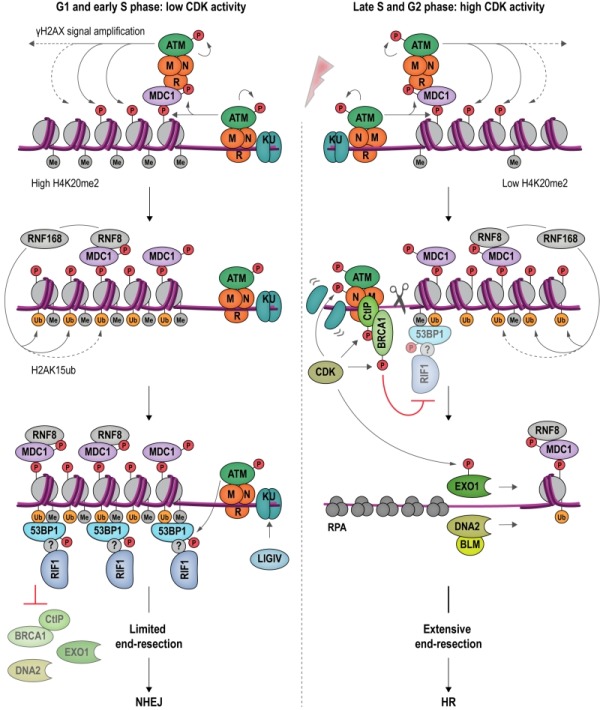
DSB formation triggers a range of protein modifications that orchestrate the cellular response and DNA repair. MRN binds DSBs and recruits apical DDR kinase ATM, which phosphorylates H2AX (γH2AX). γH2AX attracts MDC1 (Mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1), which becomes phosphorylated by ATM and binds additional MRN and ATM, providing a positive feedback loop for signal amplification. MDC1 also recruits RNF8, which cooperates with RNF168 to catalyze protein ubiquitylation at DSBs. H2AK15ub, together with H4K20me2, mediates binding of 53BP1 at DSBs. In its ATM-phosphorylated form, 53BP1 interacts with RIF1, although it remains to be determined whether this interaction is direct. The 53BP1-RIF1 complex blocks resection and inhibits BRCA1-CtIP, EXO1 and DNA2 through an as yet unidentified molecular mechanism. Attenuation of resection results in NHEJ repair in G1 and in early S phase (left). In late S and G2 phase, CDK activity rises and the H4K20me2 mark is diluted as a consequence of new histone deposition during DNA replication. CDK stimulates the endonucleolytic activity of the MRN complex, and the recruitment of BRCA1-CtIP to damaged chromatin, while 53BP1-RIF1 binding is diminished. CDK-phosphorylated EXO1 and DNA2-BLM promote long-range resection, generating 3ʹ-ssDNA overhangs, the substrate for the HR-dependent DSB repair machinery (right).
