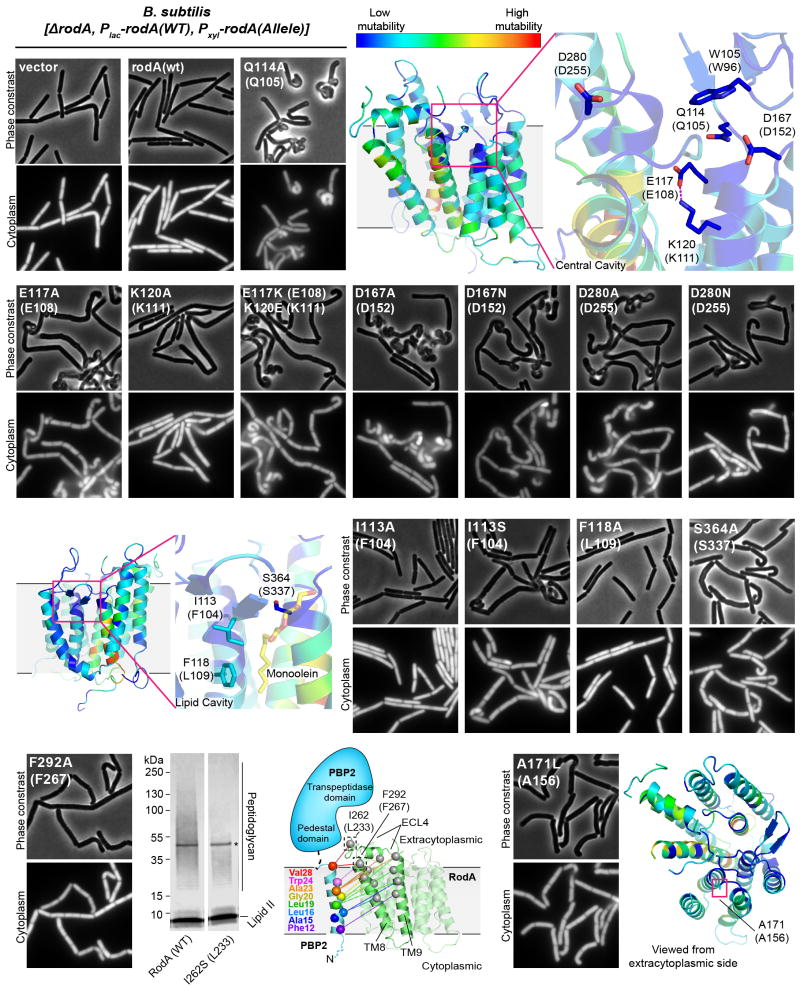
Extended Data Figure 7. Mutagenic Analysis of B. subtilis RodA function in vivo.
Micrographs of B. subtilis strains harboring an IPTG-inducible allele of rodA(WT) and PxylA-rodA(WT) or PxylA-rodA(mut). Expression was induced by growing cells in the presence of 10 μM IPTG and 10 mM xylose. The bacterial cytosol is indicated by intracellular mCherry expression (Ppen-mCherry). Mutants in the central cavity show particularly deleterious phenotypes in this dominant negative assay. Experiments were repeated independently 2–3 times with similar results. Mutation made in the predicted RodA/bPBP interface does not prevent peptidoglycan polymerization in vitro (lower left panel), representative of 2 independent experiments.