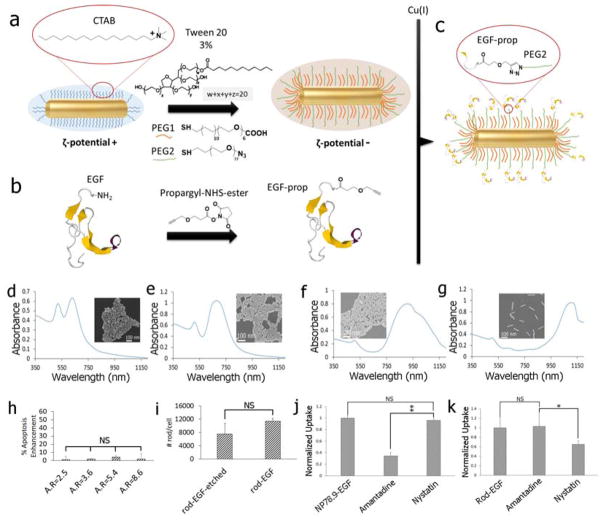
Figure 4.
a) Gold NR were functionalized with PEG1 and PEG2 in the presence of 3% v/v of Tween 20 to stabilize the NPs and to introduce binding sites for EGF (see text). b) Human EGF was modified with a terminal propargyl residue. c) The modified EGF was tethered to the binding sites of the PEGylated NR through the Cu(I) catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction. d) – g) UV-Vis spectra and SEM images of the nanorods used in this work with AR = 2.5, 3.6, 5.4, 8.6. h) Apoptosis enhancement measured for NR-EGF as function of AR under the same experimental conditions as for NP-EGF (1 nM effective EGF concentration, 4h incubation with rods). i) Average number of NR-EGF (AR = 8.6) per cell after (left) and before (right) KI/I2 etching. j) Relative uptake of (left to right): NP78.9-EGF, NP78.9-EGF + amantadine, NP78.9-EGF + nystatin into MDA-MB-468 determined by ICP-MS. k) Cellular uptake of (left to right): NR-EGF (AR=8.6), NR-EGF + amantadine, NR-EGF + nystatin. Data in (h)–(k) were collected from at least two independent experiments. Error bars show standard deviations. **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; NS = not significant.