Figure 1. Schematic diagram and pictures of the artificial feeding chamber.
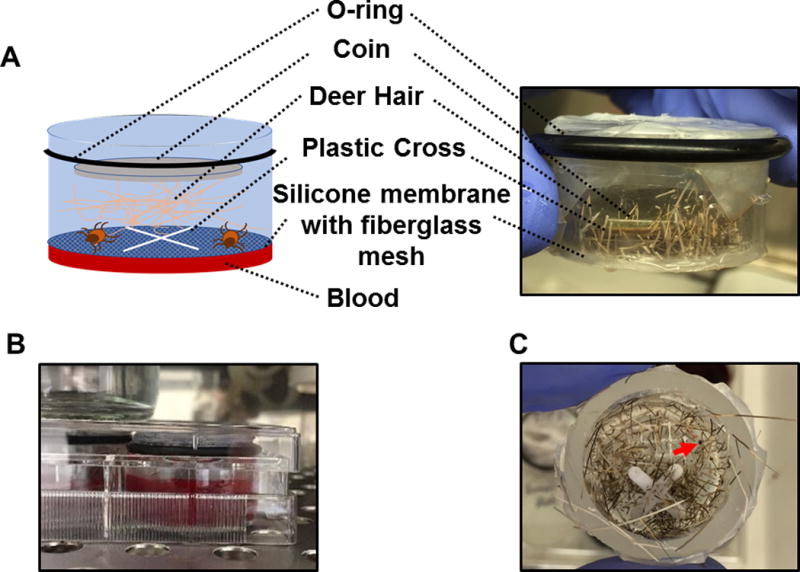
(A) A schematic diagram and picture of the artificial feeding chamber used in this study. (B) Picture showing that artificial feeding chambers were placed into a six-well cell culture plate with blood. (C) Top views of the artificial feeding chamber with the coin and deer hair removed after I. scapularis nymphal ticks were allowed to feed for 5 days. A partially engorged nymph is indicated by the arrow.
