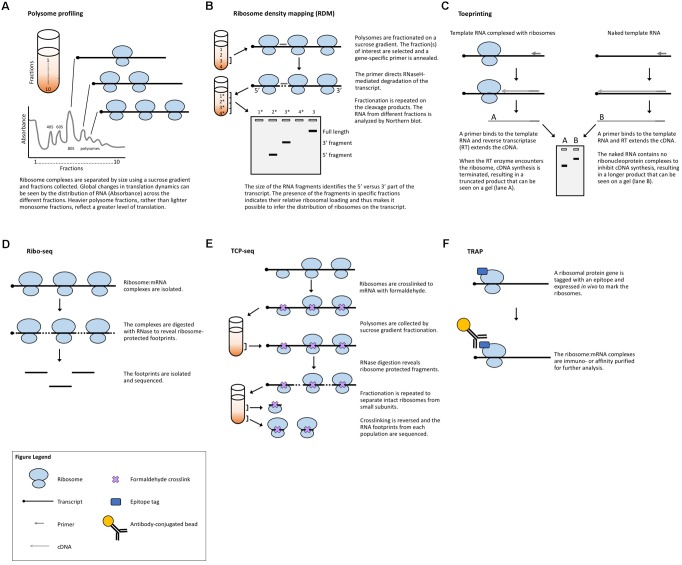
FIGURE 2.
Methods that measure ribosome:mRNA interactions. (A) Polysome profiling analyzes ribosome loading by differential centrifugation. Polysome profiling can measure global translation dynamics or, when followed by qRT-PCR, microarray, or RNA-seq, individual or genome-wide changes in ribosome loading. (B) Toeprinting utilizes gene-specific priming of the products of RT to look for premature termination due to the ribosome complex. (C) Ribosome density mapping utilizes site-specific RNaseH degradation and differential centrifugation to deduce the location of ribosomes on a transcript. (D) Ribo-seq employs RNase digestion to reveal ribosome footprints for sequencing. (E) TCP-seq uses formaldehyde to crosslink ribosome:mRNA complexes and analyzes footprints from both complete ribosome complexes and small subunit complexes. (F) TRAP utilizes affinity purification to isolate ribosome-bound transcripts for sequencing.