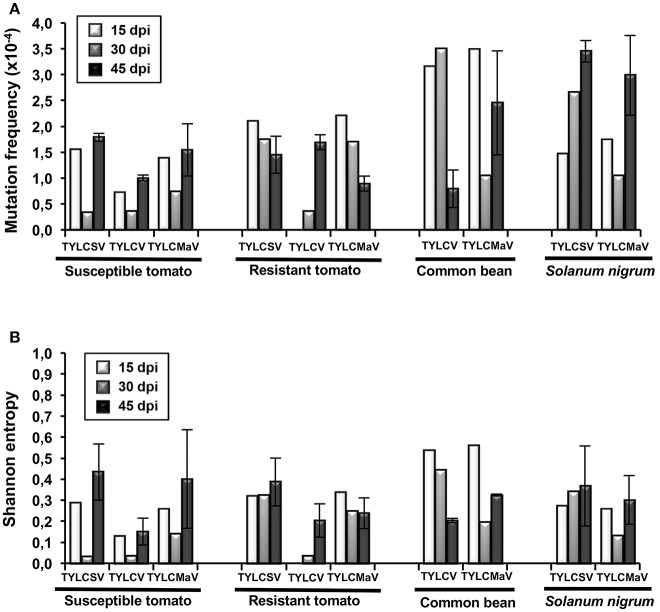
Figure 4.
Complexity and heterogeneity of begomovirus quasispecies of tomato yellow leaf curl Sardinia virus (TYLCSV), tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) and tomato yellow leaf curl Malaga virus (TYLCMaV) in quasi-isogenic susceptible (ty-1/ty-1) and resistant (Ty-1/ty-1) tomato, common bean, and Solanum nigrum plants. DNA from young apical leaf samples of the same infected plant per virus-host combination collected at 15, 30, and 45 days post-inoculation (dpi), and of a replicate plant of each virus-host combination at 45 dpi, was amplified by rolling circle amplification (RCA) and the viral DNA products cloned. Sequences of 1,437 nucleotides for TYLCSV, 1,438 nucleotides for TYLCV, and 1,429 nucleotides for TYLCMaV from molecular clones (approximately 20 per quasispecies) were aligned and compared to their consensus sequences. Only mutations (base substitutions and indels) relative to the consensus sequence of each quasispecies were computed. (A) Mutation frequencies (mutations per nucleotide) were calculated for each quasispecies. (B) Normalized Shannon entropy estimated for each begomovirus quasispecies at the indicated d of experimental evolution. The formula − [Σi (pi x lnpi)/lnN] was used, where pi is the frequency of each sequence in the mutant spectrum and N is the total number of sequences compared.